Automotive
The automotive industry is a key pillar of Mexico's economy, ranking among the world's largest vehicle manufacturers and auto parts producers. Home to major global brands such as General Motors, Ford, Nissan, Toyota, Volkswagen, BMW, Audi, Honda, and Volvo, the sector has seen remarkable growth over the past decades, attracting substantial foreign investment.
Contributing approximately 3% to the country's GDP and generating over 1.8 million jobs, the industry plays a crucial role in economic development. Producing more than 4,000,000 units annually, with approximately 80% of these units being exported, Mexico has established itself as the seventh-largest vehicle producer and the fourth-largest car exporter globally, with a strong to the United States and Canada, followed by Europe.
Some Hard Facts
- 4thlargest automotive exporter worldwide
- 7thlargest automotive producer worldwide
- 3% of Mexico’s GDP is the automotive industry
- 1.8 Mio.+ people work in the automotive industry
- 70% are exported, mainly to the U.S. Market
- 31 OEM automobile manufacturers of light and heavy vehicles in Mexico
- 600 tier 1 supplying and supporting OEM with regional content

Mexico's Automotive Industry in 2024
Mexico's automotive industry attracted $7.4 billion USD in foreign direct investment in 2023, a 57.4% increase from 2022—more than any other sector. The industry remains a key economic driver, employing over 1.8 million people and contributing 3% to the country's GDP.
Indeed, in the last two years there was almost a 10% increase in vehicles and motor parts and 17% advance in mechanical equipment; 17 of 100 new light vehicles sold in the U.S. were assembled in Mexico by American, Japanese and European OEMs. As Mexico solidifies its role as a global automotive hub, continued investment, nearshoring, and the shift to EV production will shape its competitive position in the coming years.
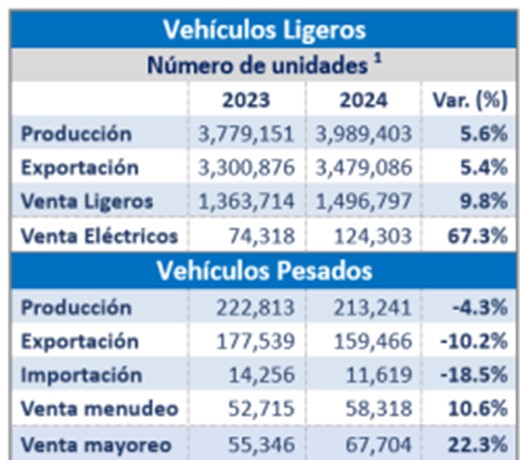
Regarding sales, Mexico's automotive industry rebounded to pre-pandemic levels, with vehicle production reaching 3.8 million units (+14.2% year-over-year) in 2023. Local car sales surged by 24.4% to 1.4 million units, while exports increased by 15.2% to 3.3 million vehicles.
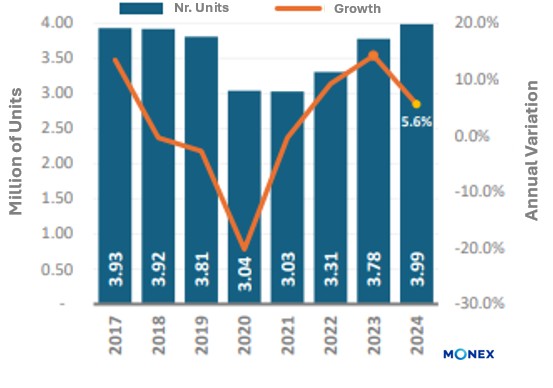
In 2024, Mexico's automotive industry achieved a new production milestone, manufacturing 3.99 million light vehicles, a 5.6% annual increase, and making Mexico one of the world's leading automotive manufacturing hubs. Although this surpassed the previous record set in 2017 (3.93 million), it fell slightly short of the projected 4.0 million vehicles anticipated by the Mexican Automotive Industry Association (AMIA).
The leading manufacturers were General Motors, producing 889,072 units (+23.0%), and Nissan, with 669,941 units (+8.8%), together accounting for 39.1% of total production.
Production total cars light 2017 – 2024
State-Level Leadership in Automotive Manufacturing
The top states driving automotive production and exports were:
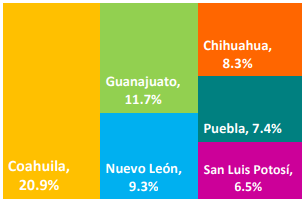
These regions play a crucial role in Mexico's position as a global automotive manufacturing hub.
Mexico's Automotive Industry Projects 2024
OEMs and suppliers are expanding operations in Mexico as part of nearshoring strategies to mitigate global supply chain risks.
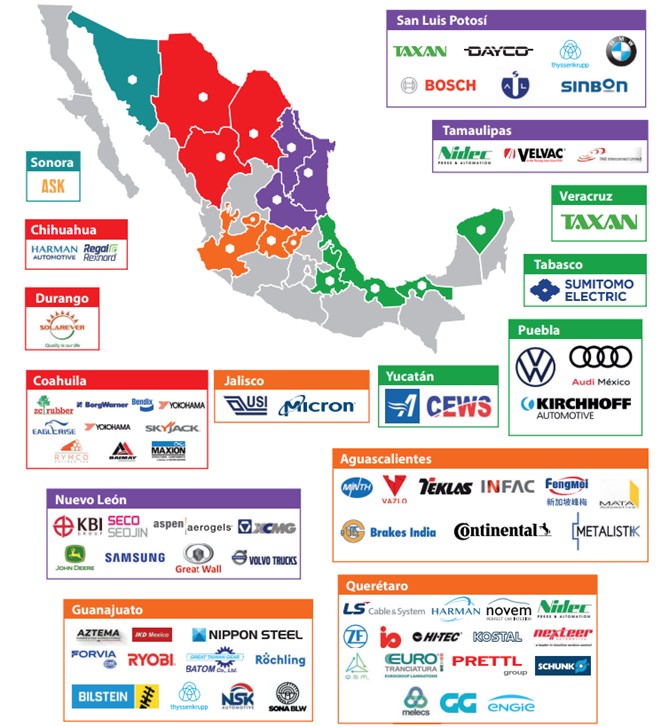
Major investments include:
- ZF Friedrichshafen ($1 billion USD investment) for R&D in autonomous vehicles and electromobility projects in Monterrey, Ciudad Juárez, and Saltillo.
- KOSTAL opened a new production facility for electric vehicle (EV) on-board chargers in Querétaro, modeled after its Chinese plant, primarily to serve U.S. manufacturers.
- BMW invests into a new manufacturing plant in San Luis Potosi with an investment of $860 Mio. USD
- Volkswagen into the plant in Puebla with an investment of $763 Mio. USD
- Nissan in Aguascalientes with an investment of $700 Mio. USD
- Kia in Pesqueria (Nuevo Leon) with an investment of $408 Mio. USD
- Toyota in Guanajuato with an investment of $328 Mio. USD
- Navistar in Escobedo (Nuevo Leon) with an investment of $120 Mio. USD
- Audi in San Jose, Chiapas
Growth Outlook 5 years
Mexico’s automotive manufacturing sector is projected to grow between 15% and 20% annually, significantly outpacing the global industry’s expected 2-3% growth rate. This expansion is fueled by nearshoring trends, increased foreign investment, and supply chain integration under the USMCA. However, the rapid growth presents challenges for public infrastructure, as cities will need to enhance services to accommodate industrial expansion.

In the electric vehicle (EV) market, Europe saw a 50% share of EV and hybrid sales in 2024, while North America’s consumer shift is expected to take clearer shape in 2025. Despite the global push for EV adoption, full electrification in North America by 2030-2040 remains unlikely, with internal combustion engine vehicles continuing to play a significant role.
Additionally, sustainability efforts in manufacturing are gaining momentum. Companies like Ball Corporation are setting ambitious targets to reduce CO₂ emissions by 55% and achieve 100% renewable energy use by 2030. Meanwhile, circular economy principles are evolving beyond the traditional "Reduce, Reuse, Recycle" model to include product repairability as a key sustainability strategy.
Mexico’s strategic advantages, including a skilled workforce, trade agreements, and industrial infrastructure, continue to attract global manufacturers, reinforcing its role as a key player in the automotive industry.
Vehicle Exports
Mexico's exports of light vehicles rose by 5.4% annually, reaching 3.5 million units. The majority (79.7%) were destined for the United States, followed by Canada (8.5%). General Motors led exports with 830,820 units (23.9% market share), followed by Nissan (13.1%) and Ford (10.9%). Notably, Honda saw the highest export growth, increasing shipments by 50.7% compared to 28.0% in 2023. The top exported models included the Equinox SUV, Tacoma, Sentra, HR-V, and Maverick.
Challenges in Heavy Vehicle Production and Exports
Contrary to the growth in light vehicles, the heavy vehicle segment saw declines. Production dropped by 4.3%, and exports fell by 10.2%, primarily due to weaker demand for freight trucks (-24.7%) and passenger buses (-34.8%). The United States, which accounts for 95.5% of Mexico’s heavy vehicle exports, recorded a 10.7% decrease in imports from Mexico, further impacting the sector.
Majority car exports to the United States
As mentioned before, almost 80% of the models are exported to other countries, particularly to the United States. Thus, Mexico's automotive industry's dependency on the United States market is significant, and any changes in the United States' economic policies could have a significant impact on the countries automotive industry's future growth and development. Furthermore, the North American supply chain has been a crucial factor in Mexico's automotive industry's growth. Many of the vehicles produced in Mexico are assembled using components manufactured in the United States and Canada. This integrated supply chain has made it more efficient for automakers to produce cars in Mexico and export them to the United States.
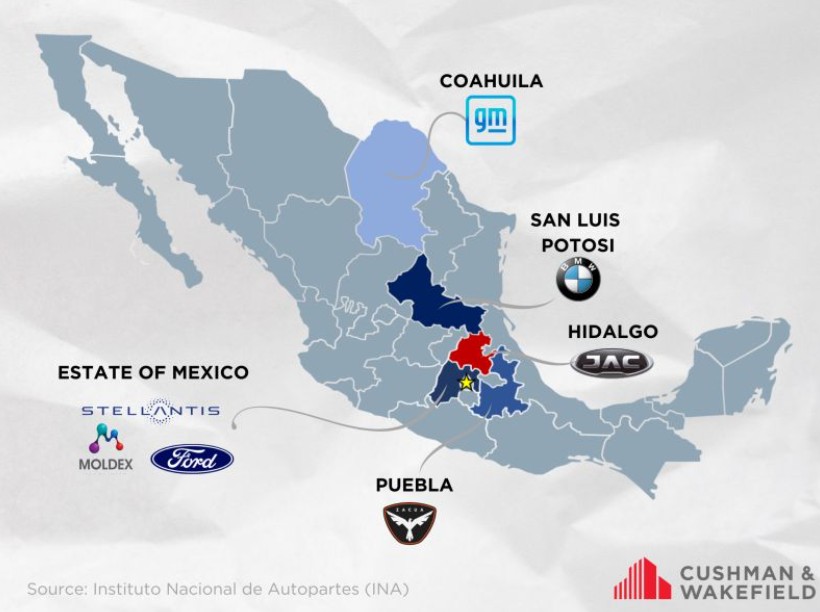
Where are the Car Manufacturers in Mexico
Mexico's favorable geographical proximity to the United States, cost-effective labor, participation in the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), and its free trade agreements with several nations have positioned it as an appealing destination for automotive manufacturers to establish their operations.
The country is home to over 2,200 automotive plants at all levels of the supply chain—OEM, Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3. This robust infrastructure positions us as a global powerhouse for automotive manufacturing and nearshoring.
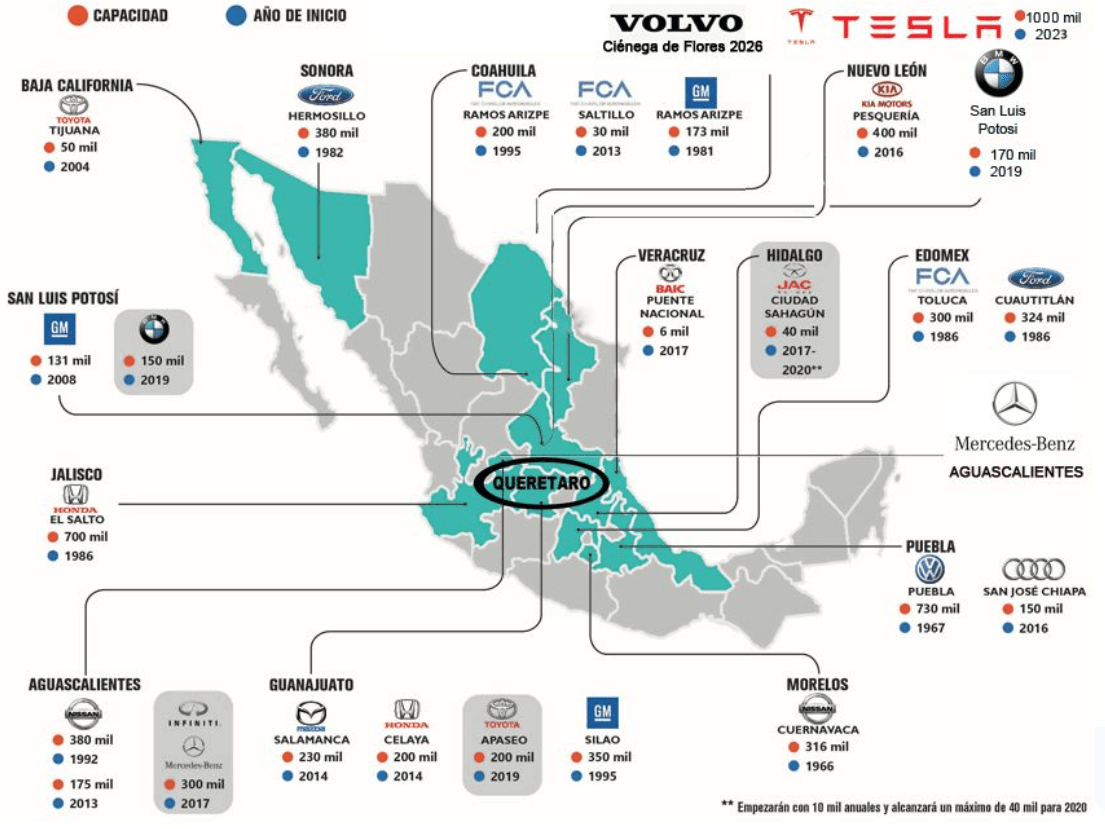
Northern Border Region: Are the regions along the border with the United States and includes the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, and Tamaulipas. It is home to several assembly plants and supplier parks, and is a major hub for trade between Mexico and the United States. Especially Monterrey has been experienced a huge boom of new suppliers thanks to the investment of Tesla.
Bajio Region: Is located in central Mexico and includes the states of San Luis Potosi, Queretaro, Aguascalientes and Guanajuato. The region is home to several automotive assembly plants and supplier parks and has become a major hub for automotive production in Mexico.
Central Mexico: Includes the states of Mexico, Morelos, Puebla, and Hidalgo and is home to several automotive assembly plants and supplier parks. This region is well-known for its expertise in manufacturing automotive components such as wiring harnesses and electrical systems.
Pacific Coast: Includes the states of Jalisco and Colima is known for its expertise in manufacturing automotive components such as aluminum parts and electronic systems.
Southeast Mexico: Includes the states of Veracruz, Tabasco, and Campeche and is known for its expertise in manufacturing automotive components such as powertrain systems and engines. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that automotive suppliers may also be situated in other regions across Mexico, and the distribution of suppliers may evolve as the industry progresses. Moreover, Mexico is actively investing in the advancement of electric vehicles, with several companies strategically planning to manufacture EVs within the country in the forthcoming years.
Electric Cars
Automakers are investing heavily in EV production to meet global demand:
- Volkswagen is investing nearly $1 billion USD to convert its Puebla plant for EV production.
- BMW will invest $860 million USD in its San Luis Potosí plant to manufacture fully electric "New Class" models starting in 2027.
- Ford expanded production of the Mustang Mach-E by 20.5% in 2023, reaching 94,000 units.
- General Motors began production of the Equinox EV and Blazer EV in Ramos Arizpe in October 2023, following a $1 billion USD plant expansion.
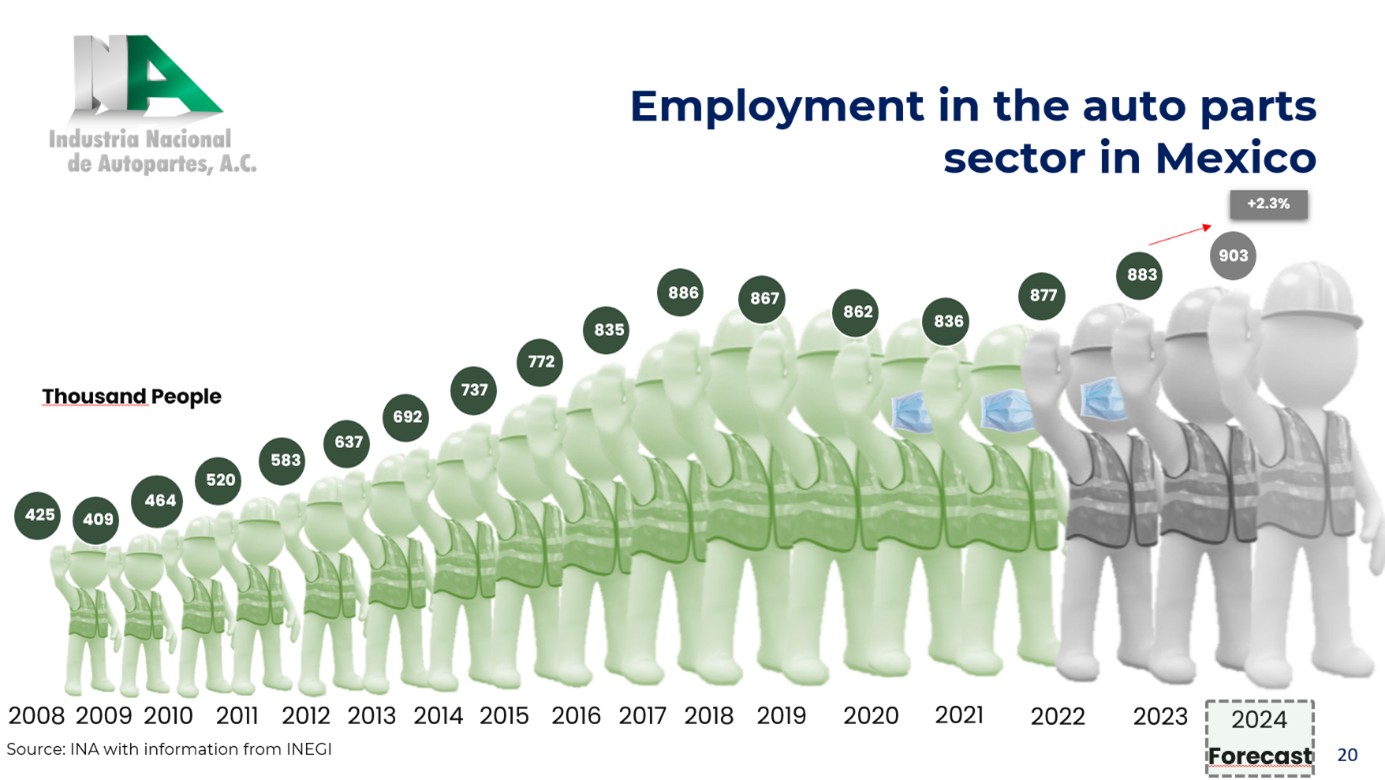
Employment in the Automotive Industry
Mexico's automotive industry remains the backbone of the national economy, accounting for 3% of GDP and employing over 1.8 million people. In 2024, automotive exports contributed $177.9 billion, a 3.1% increase from the previous year. The country maintained a strong manufacturing base, utilizing 97.4% of plant capacity, with a 3.8% annual expansion in transport equipment production.
As Mexico continues to consolidate its role as a global automotive powerhouse, the industry's adaptability to emerging trends—particularly electrification and nearshoring—will determine its long-term competitiveness in international markets.
Brands in Mexico
Nissan remained the market leader in 2023, increasing sales by 42.7% and securing a 17.7% market share, followed by General Motors and Volkswagen. The most popular models included the Nissan Versa, NP300, Kia Seltos, and Volkswagen Taos. Chinese manufacturers gained significant traction, with a combined 10% market share.
- Chirey recorded a remarkable +343.9% sales growth.
- Motornation (BAIC, JMC, Changan) grew by +52.8%.
- MG Motor led in absolute sales among Chinese brands (60,128 units, +25%), surpassing Ford, Hyundai, and Renault.
When it comes to automotive manufacturing in Mexico, the primary car producer in terms of exports is the American company GM, accounting for nearly 27% of the total exports, followed by
Notably, Mexico is actively investing in the advancement of electric vehicles, with numerous companies planning to manufacture EVs within the country in the near future. Consequently, Mexico has steadily expanded its production capacity in recent years, leading to a notable presence of 93 out of the top 100 global automotive parts manufacturers operating within its borders.
Producing diverse range of cars
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic causing a slowdown in 2020, the industry is expected to continue to grow in Mexico in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for vehicles in North America and the development of new technologies. Indeed, many automakers have manufacturing facilities in Mexico and produce a wide range of vehicles, from small cars to large trucks and SUVs.
Mexico's car industry also produces luxury cars, such as the BMW 3, Audi Q5, Series, and Mercedes-Benz C-Class, as well as electric vehicles, such as the Chevrolet Bolt and the Nissan Leaf. Overall, Mexico's car industry offers a diverse range of vehicles for both domestic and international markets.
Tier 1, 2 and 3 car suppliers
Mexico boasts a robust automotive supplier base, encompassing both Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, which play a crucial role in producing a diverse range of vehicle components. With over 600 Tier 1 automotive suppliers currently operating in the country, Mexico directly contributes to the supply chain by providing parts and components to automakers.
Notably, the recent surge in nearshoring has led to a significant increase in the number of new Tier suppliers in Mexico, spurred by the "Tesla" effect, as suppliers strive to be near their customers and leverage the advantages offered by the Immex program and the availability of skilled labor.
Among the prominent Tier 1 suppliers in Mexico are Magna, Denso, Continental, Bosch, and Aptiv, renowned for their expertise in the automotive industry. It is worth mentioning that automotive suppliers are spread throughout Mexico, with certain regions being recognized for their automotive industry clusters, thus facilitating efficient collaboration and resource allocation.
Government Incentives for Auto Industry
The government has demonstrated its support for the automotive industry by implementing favorable policies aimed at attracting foreign investment, such as tax incentives and R&D assistance. These initiatives provide financial resources, training programs, and technical support to assist companies in developing innovative technologies and enhancing their products and processes. Nonetheless, the automotive industry in Mexico encounters certain challenges, including concerns regarding worker safety and environmental impact, as well as the necessity to enhance infrastructure and decrease reliance on imported components and parts.
Furthermore, the government has yet to introduce environmental incentives aimed at encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies and mitigating the environmental footprint of the automotive sector. These incentives could involve tax credits, subsidies, and other advantages for companies investing in sustainable technologies and adopting environmentally friendly practices. Despite these challenges, Mexico's automotive industry is poised for a promising future, with sustained investment and growth anticipated in the years ahead.
Aerospace
Even though the aerospace manufacturing industry in Mexico is relatively young compared to other markets, it is growing exponentially. Thus, the Mexican Government launched various programs to create employment opportunities, including business incentives, new workforce training programs, and new universities.
Some Hard Facts
- 14th largest supplier globally
- 6th largest exporter worldwide in aeronautic
- 300+ aerospace companies exist in Mexico
- 90 companies are located in Queretaro which is the mainspot for aerospace
- $8 billion has been exported to the US in 2022
Aviation and Aerospace Manufacturing in Mexico
Mexico is one of the six most important suppliers to the U.S. aerospace sector. The aerospace industry in Mexico has experienced significant growth in recent years with a strong presence in the manufacture and assembly of aerospace components, such as wiring systems, interiors, and composite materials. In numbers, the aerospace sector has been growing 17.2% on average per year and moved from tenth to sixth place among the countries that export the most to the aeronautical industry.
The industry has been growing steadily since the 1980s and has experienced significant expansion in recent years, driven by factors such as the country's strategic location, skilled labor force and favorable business environment like the strong government support.
Mexico’s aerospace sector is actively working to strengthen its position in global supply chains, attracting companies exploring local operations and those committed to finding alternative suppliers. Organizations like FEMIA are playing a crucial role in facilitating this transition. While Boeing’s recent challenges have had some impact on production schedules, Mexico’s well-diversified aerospace industry has mitigated major disruptions. Stricter quality standards resulting from these issues could benefit Mexico, reinforcing its reputation for high-quality manufacturing and opening new opportunities for component production.
Locations of Aerospace companies
Mexico’s aerospace industry is experiencing a period of significant expansion, driven by nearshoring trends, strong manufacturing capabilities, and increasing foreign investment. The sector has evolved beyond basic manufacturing to include research, development, and innovation, positioning Mexico as a key global player. With over 300 aerospace companies—80% focused on manufacturing and the rest on maintenance, design, engineering, and operations, the industry has seen impressive growth. The other 20% offer design and engineering services, as well as maintenance, repair and operations (MRO).
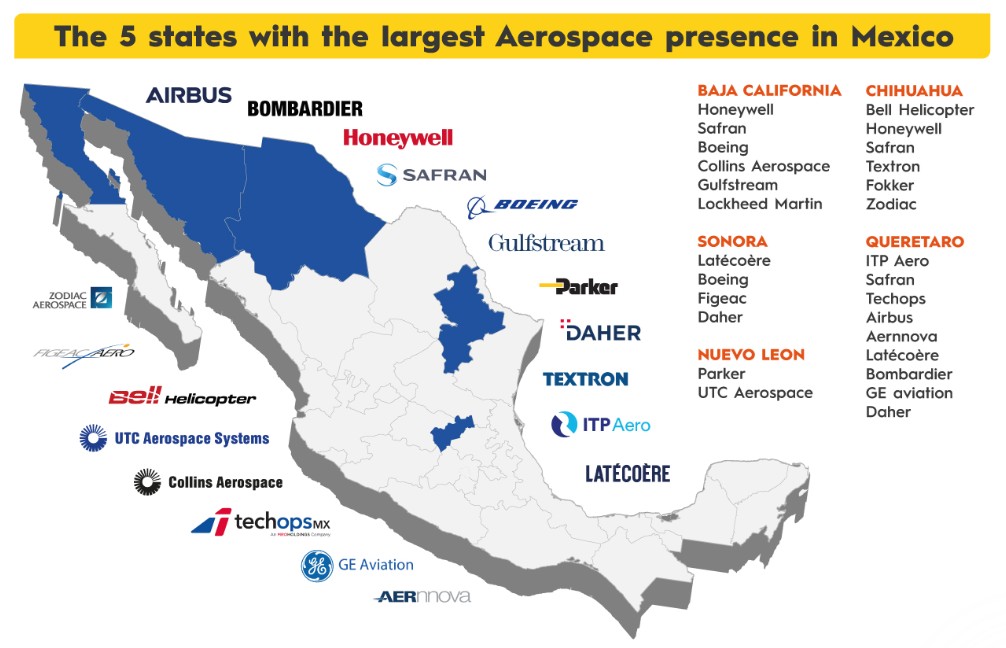 Mexico is home to many companies involved in aerospace manufacturing, including international firms like Safran, Bombardier, and Airbus. Out of the yearly 100,000 students, a large pool of highly skilled engineers and technicians have been trained in aerospace-related fields. In 2023, economic activity in this sector increased by 18%, with 2024 exports projected to surpass $10 billion. Major aerospace hubs like Querétaro, Baja California, Chihuahua, and Nuevo León continue to attract international investment, particularly from the U.S., Canada, and France.
Mexico is home to many companies involved in aerospace manufacturing, including international firms like Safran, Bombardier, and Airbus. Out of the yearly 100,000 students, a large pool of highly skilled engineers and technicians have been trained in aerospace-related fields. In 2023, economic activity in this sector increased by 18%, with 2024 exports projected to surpass $10 billion. Major aerospace hubs like Querétaro, Baja California, Chihuahua, and Nuevo León continue to attract international investment, particularly from the U.S., Canada, and France.
The nearshoring wave has created new opportunities, as global OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers seek to regionalize supply chains for cost efficiency, risk management, and quality control. Carlos Robles, president of FEMIA, highlights how logistical challenges and geopolitical shifts are pushing aerospace companies to relocate production closer to key markets. The demand for Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) services, as well as aerospace components for commercial and space applications, is rising, with Mexico already involved in international projects, including NASA initiatives.
Queretaro – the Hub of Aerospace
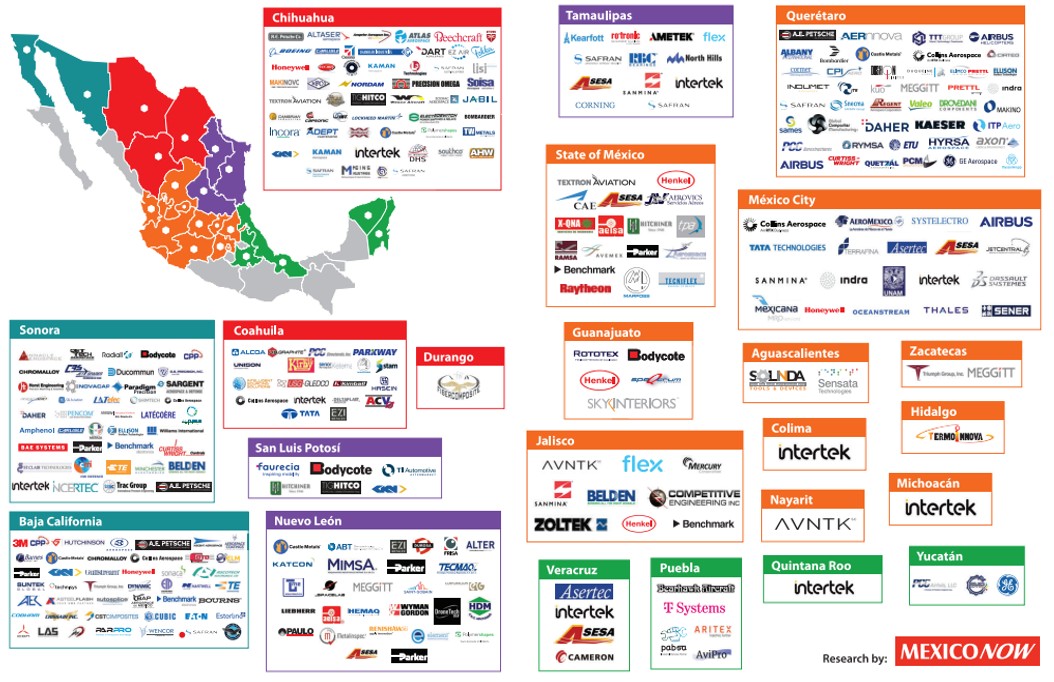
In the last 20 years, many Aerospace companies have moved a significant amount of manufacturing to Mexico. Important regions of production are the Northwest, the Northeast and Central Mexico. Out of the over 300 companies in that sector, the main spot is Queretaro (Central Mexico) with over 90 companies.
Indeed, Queretaro has emerged as a strong player in the aerospace industry and ranks 8th as one of the cities worldwide with the best FDI performance in the aerospace sector. It opened the first specialized aeronautics university a few years ago, attracting companies such as Bombardier. Queretaro is located in the center of Mexico, which provides easy access to major cities and transportation hubs. The city with only a bit more than 1 million habitant attracts with the following facts new foreign investment in the Aerospace industry.
What aerospace products do they produce?
OEMs, Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, MRO and design centers that serve this industry are clustered around large manufacturers and producing small components, actuators, composites and castings, but also produce complex devices such as flight control and avionics and even turbines, landing gear and engine components.
- 72% in manufacturing
- 13% in design and research
- 11% in maintenance and repair
- 4% other
80 companies and support entities are broken down in following sectors
- 2 OEMs
- 26 Tier 1&2
- 5 MRO
- 5 Special Processes
- 4 Raw Materials
- 19 General Services
- 12 Research Centers
- 12 Academic Institutions
Exports Aerospace
Mexico remains a key global player, with approximately 368 aerospace facilities, primarily focused on manufacturing (80%), Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) (11%), and Engineering and Design (9%). These facilities span 19 states and employ around 57,000 workers.
In 2023, Mexico’s aerospace exports reached $9.4 billion, a 16% increase from $8.1 billion in 2022, according to the U.S. Department of Commerce. However, the industry’s supply chain structure resembles an inverted pyramid, with a shortage of Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers creating bottlenecks that hinder the growth of Tier 1 and OEM companies. Despite these challenges, aerospace firms in Mexico are working to strengthen the ecosystem and capitalize on market.
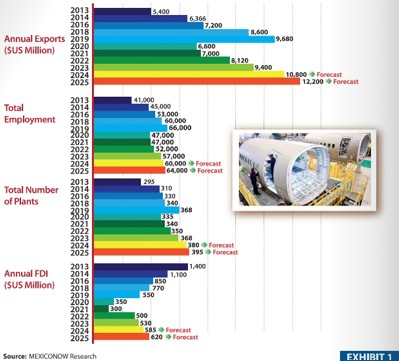
Continuing to grow in 2024 and 2025
Mexico’s aerospace industry is poised for a significant upswing in 2024 and 2025, with exports expected to reach $10.8 billion this year and $12.2 billion next year—marking a 13% growth. The sector is projected to expand to 395 facilities employing 64,000 workers, supported by approximately half a billion dollars in foreign direct investment.
Challenges Aerospace
However, several challenges persist, particularly supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and high operational costs. The industry is grappling with material shortages, exacerbated by global logistics bottlenecks, including disruptions in the Red Sea.
Skilled Labor Force: While Mexico’s competitive labor costs and strong trade agreements provide an advantage, the country must invest in education, technology, and infrastructure to sustain its upward trajectory. Indeed, the sector faces a pressing need for skilled labor, with industry estimates suggesting that 40,000 aerospace engineers will be required over the next two decades.
Sustainability: Sustainability is another major concern, as companies work to reduce their carbon footprint amid Mexico’s restrictive energy policies. While solar energy presents a viable solution, government-imposed limitations on industrial self-generation are hindering progress.
Market Volatility: Other major challenges for 2025 are market volatility, driven by geopolitical tensions and shifting trade policies, and the need for Mexico to be recognized not just as a manufacturing hub but also as a center for research, development, and engineering innovation.
Government Support:Internally, the aerospace industry faces hurdles in securing strategic government recognition and support, which would provide crucial incentives and stability, as well as improving access to competitive financing. Without better financial mechanisms, the cost of capital remains a constraint on growth and technological advancement.
Water & Electricity:The lack of local suppliers for high-tech aerospace components, infrastructure constraints in power and water supply, and an insufficient number of highly skilled engineers could limit growth.
Despite these obstacles, the aerospace industry remains resilient, with strong nearshoring potential and increasing demand for MRO services and aircraft modifications. The incoming administration under President Claudia Sheinbaum will play a crucial role in shaping industrial and energy policies to capitalize on Mexico’s manufacturing potential. With strategic investments, innovation, and policy support, the sector is well-positioned to overcome current challenges and continue its upward trajectory.
In addition, companies are diversifying their supplier base and investing in local production, yet these shifts require substantial capital and time. The demand for high-precision processes, such as Nadcap-certified welding, 5-axis machining, and heat treatment, continues to grow, urging OEMs and Tier 1 companies to collaborate with local suppliers for certification and validation.
Governments Incentives in the Aviation and Aerospace Industry
The Mexican government has recognized the potential of this industry and has implemented several measures to support its development. In the late sixties, the Mexican Government’s Maquiladora Export Program (now known as the IMMEX Program) began laying the foundation for this industry. It is mostly responsible for expanding industrialization, employment opportunities and most importantly, allowing the importation of goods to be assembled and exported without import duties or taxes.Aerospace companies have taken advantage of thesemanufacturing opportunitiesin Mexico.
In addition, the Mexican Government launched various other programs to create employment opportunities, including business incentives, new workforce training programs, and new universities.
Initiatives by the Mexican government
- they established research and development programs in collaboration with the aerospace industry which aim to develop new technologies and processes that can be used in the manufacturing of aerospace components.
- They invested in infrastructure projects that support the aerospace industry which includes the construction of airports, the expansion of existing airports, and the development of aerospace parks.
- They implemented training and education programs to develop a skilled workforce for the aerospace industry. This includes the establishment of specialized schools and training centers that offer courses in aerospace engineering and manufacturing.
- They stablished partnerships with other countries in the aerospace industry. These partnerships include joint research and development projects, technology transfers, and collaboration on international aerospace projects.
Overall, the Mexican government has taken significant steps to support the growth and development of the aerospace industry in the country. These efforts have helped to attract foreign investment, create jobs, and establish Mexico as a key player in the global aerospace market.
FDI in the aerospace industry
Thanks to its proximity to the United States, many Asians companies see the ideal place in Mexico to start their production. Other, large foreign aerospace companies such as Boeing, Airbus, Safran, Bombardier, Siemens and Thales already have operations in Mexico that could be expanded in view of the growing trend to relocate production lines with a regional and not necessarily global perspective.
The development of Industry 4.0 in the country as well as the consolidation of industrial clusters in areas of Querétaro, Chihuahua, Nuevo León and Guanajuato make Mexico an attractive place for foreign investment in the aerospace sector. Indeed, the trend of foreign investment in aerospace manufacturing in Mexico could increase due to the interest of international companies in the sector. These companies are looking to relocate their production to North American soil, a region increasingly integrated industrially by the Free Trade Agreement between Mexico, the United States and Canada.
Apparel and Textile
As Mexico’s fourth-largest manufacturing industry, the apparel/clothing, and textile manufacturing, accounts for 3.7% (1.3% in textiles and 2.4% in apparel) of Mexico’s manufacturing GDP. Volkswagen, Mercedes Benz, BMW and others are getting automobile filters, airbags, seat covers, doors, bands and cables manufactured by upgraded textile facilities in Puebla, Mexico.
Some Hard Facts
- 4 billion USD growth between 2021 - 2026
- Over 500,000 employees in the apparel & textile sector
- 75% account for the apparel sector
- 400+ companies with 130,000 emploees are Immex Program certified

Apparel & Textile Manufacturing in Mexico
The textile industry has a long history in Mexico and is a significant sector of the country's economy and has been attracting manufacturing investment for the fabrication of textiles for many years. Presently, there are over several hundred textile companies established in Mexico which create over 500,000 working places in this sector. Mexico ranks as the world's seventh-largest textile producer, with a notable concentration of production in the states of Mexico State, Mexico City, and Puebla. The country's textile industry encompasses a diverse array of products, including home textiles, apparel, and technical textiles. Mexico has garnered a reputation for manufacturing top-tier knitwear, denim, and workwear, which enjoy significant global demand due to their exceptional quality.
Thanks to Mexico’s large and skilled workforce with experience in apparel production, including design, cutting, sewing, and finishing, they have attracted companies from around the world to set up their manufacturing operations in Mexico. Thus its, not surprisingly that the apparel industry became a key player in the maquila program and accounts for around 75% of the total production and is therefore the largest segment.
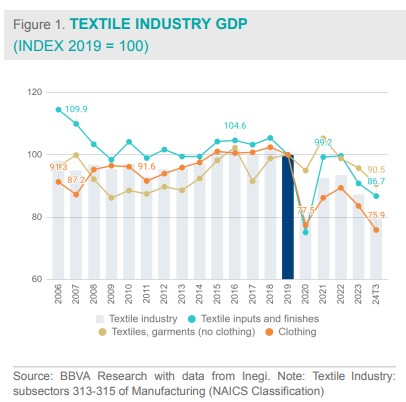
Declining GDP
The textile industry contributes 0.4% to the national GDP and 1.8% to the manufacturing GDP. By the end of Q3 2024, its GDP reached 95.4 billion constant pesos, 19.1% below pre-pandemic levels, with an average annual contraction of 4.2% since 2019. The apparel manufacturing sector (NAICS subsector 315) leads the industry, accounting for 55.3% of total output, followed by textile and finished inputs at 28%. As shown in Figure 1, these two subsectors have experienced the greatest decline in domestic production.
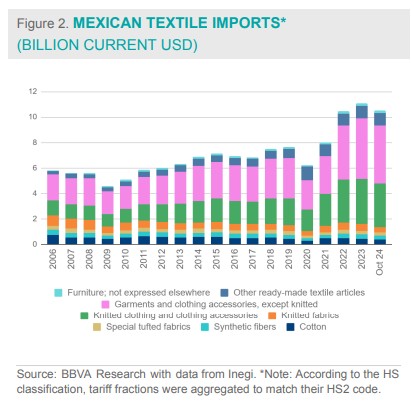
Mexico experiences a textile trade deficit
By the end of 2023, Mexico's trade deficit in goods was primarily with Asian countries, led by China, followed by Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea. In contrast, Mexico maintained a trade surplus mainly with countries in the Americas, with a significant concentration in the U.S. The surplus with the U.S. exceeded $234 billion, more than double the $104 billion deficit recorded with China in 2023.
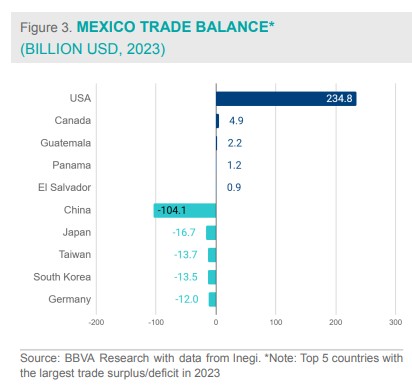
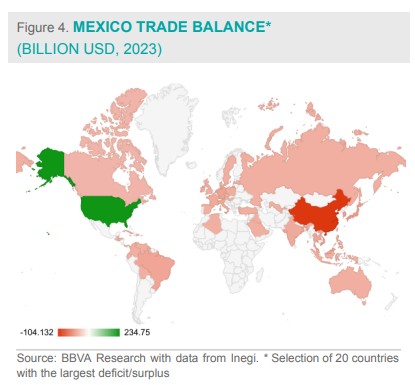
Advantages of Mexico for the apparel industry
Due to the proximity to the United States and the cheap labor force, Mexico is a significant exporter of textile products, with the United States being the largest market for Mexican textiles. Other major export markets include South America, Central America, and Canada. Thus, the Mexican government has invested heavily in its infrastructure, including transportation, communication, and technology, which has improved logistics and supply chain management for the apparel industry.
Though the main reason manufacturing apparel & textiles in Mexico is the Maquila Program which was created by the government to promote economic development and attract new foreign investors. Around 400 companies with over 130,000 employees are IMMEX-certified and take the advantage of the import duty-deferral government program.
The main competitor are the low-cost producers like China and Bangladesh, however due to the tense relation and its trade war between China and the United States, the industry continues to grow and remains an important contributor to the Mexican economy. A major challenge is the need to invest in modernizing and upgrading production facilities.
Textile Forecast Growth Mexican Market
As we can see on the graph, the textile production market share is expected to increase to USD 4 Billion from 2021 to 2026. One of the key growths is the increasing demand for textile in the automotive industry. This sector uses synthetic fibers to produce lightweight, fuel-efficient, and environment-friendly vehicles to comply with stringent regulations. Thus, the high production of vehicles which all need textiles in the interiors, will increase the demand for textiles during the forecast period.

The fiber segment, which is extensively used to produce garments, apparel, construction materials, medical dressings, and automotive interiors segment, will have a significant growth during the forecast period. For instance, silk fibers are used for applications such as tasar materials, socks, clothing, and others. The silk market in Mexico is growing at a healthy rate, given the various benefits of silk, including its suitability for all climatic conditions, quick-drying nature, durability, and softness.
Textile Relocation from Europe to Mexico
After two pandemic years, manufacturers in clothes and apparel were hoping to be able to recover in 2022. However, when Russia invaded Ukraine, manufacturers facing fresh challenges from the energy crisis to fluctuating raw materials prices to the global supply chain’s transformation. Many European producers such as Spain, Portugal or French are very dependent on the gas to produce Apparels & Textiles, however they are facing huge problems due to the increased electricity costs. And as there is no end in sight, many companies considering to relocate their production places – which could be in favor of Mexico.
Appliances
Several large international appliance manufacturers have production facilities in Mexico, including Samsung, LG, Whirlpool, General Electric, or LG. These companies have taken advantage of Mexico's proximity and access Several large international appliance manufacturers have production facilities in Mexico, including Samsung, LG, Whirlpool, General Electric, or LG. These companies have taken advantage of Mexico's proximity and access to the market of the United States, relatively low labor costs, and favorable business environment.
They are producing various products such as freezers, dishwashing machines, washing machines, ovens and refrigerators.
Some Hard Facts
- 2nd largest exporter of appliances to the United States
- 5th largest producer of household appliances
- 14,800 million dollars worth of production
- 8% growth in 2023 projected
- Over 40% electrical appliances are produced in Nuevo Leon
- 3,500+ appliance companies in Mexico
- 60% export share in TV to the United States
- 85% of the appliance exports go to the United States

Appliance Industry Mexico
Many appliance products are being manufactured in Mexico now as well. As manufacturing costs continue to rise in China, producers are moving their operations to Mexico for a variety of cost-efficient reasons.
The Mexican government has taken several efforts to encourage investment in the appliances industry, including offering tax incentives named as “Immex-Program”, and investing in infrastructure improvements to support manufacturing operations and decrease supply chain costs. As a result, the appliances industry has become an important part of Mexico's manufacturing sector and a key driver of economic growth. Thus, it is not surprisingly that Mexico is – beside Japan or England – one of the biggest exporters of appliances in the world, major appliances exports include laundry appliances (washers and dryers), range stoves and fridges and freezers.
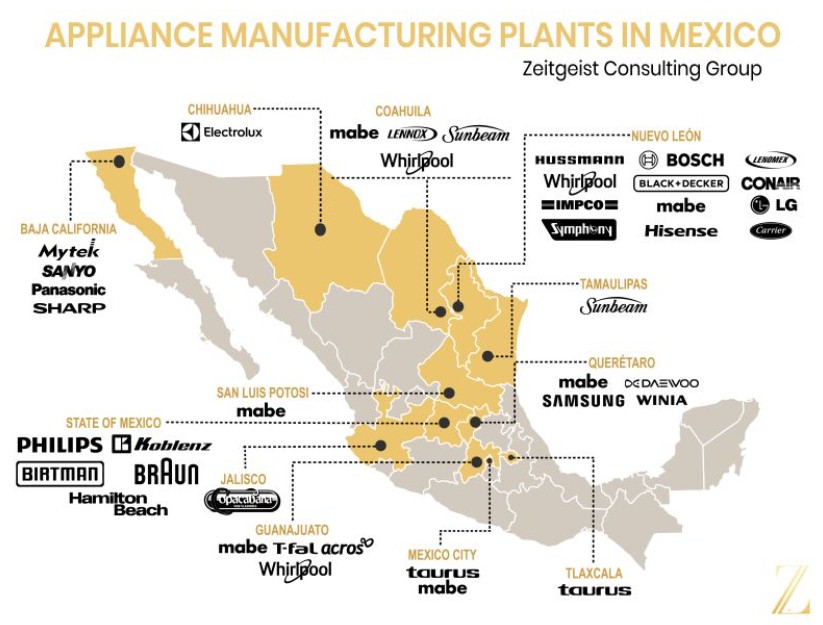
The household appliance industry in Mexico has experienced an astonishing growth over the past three years as well, primarily due to wage inflation and the trade conflict between China and the United States. Based on various projections, the industry will continue to grow in 2023 by 8% thanks to the over 500 appliance companies and new entrants Another factor is the OEM’s requirement for just-in-time delivery, which requires the supplier to be within a 1-2 hour driving distance from the OEM’s assembly plant – Mexico can provide that due to the modern infrastructure and proximity to its final customers in the United States. However, Mexico has still lots of potential to improve its numbers; Household appliances manufacturers currently occupy only 12% of existing industrial areas.
Locations of the appliance manufacturers
There are around 3,500 companies that belong to the home appliance industry, mainly located in the states Guanajuato, Baja California, Chihuahua, Jalisco, State of Mexico and Mexico City. According to Clelac, Guanajuato leads the list nearly 600 establishments, followed by Jalisco with 450 and Nuevo León, with 350 companies established in the state.
Some of the most representative of the home appliance industry that are installed in Mexico are: Samsung, Whirlpool, Mabe, Carrier, Bosch, Hisense, Trane Technologies, Criotec, Dometic, among others. Mexico ranks 5th as a global home appliance supplier, with a 5.1% share. In first place is China, with 29.5%; followed by Germany, with 9%; the United States, with 5.8%; and Italy, with 5.7%.
Companies’ investments into Home Appliance
The manufacturing industry in Mexico is for refrigerators, washing machines and other household appliances almost US $15 billion dollars’ worth. In terms of production and investment, there will be a future growth of 8% thanks to the nearshoring trend. Various companies like Bosch, Danfoss, Whirlpool or Hisense announced new openings and will continue to grow during the coming years with already existing plants. In that, companies do not only want to focus on mass production but also on new technologies in the home appliance industry to stay competitive and attractive in the long term. Indeed, the smart home appliance industry is worth US $31 billion globally with an annual growth rate of 18% until 2026. Thanks to only 3 hours driving to the United States, Nuevo Leon is responsible for over 40% of the appliance production and generates over 30,000 direct jobs in that region. And in the coming years, this figure will increase by up to 20% thanks to the arrival of new investments.
Even though Mexico is a very attractive location based on low cost, many companies are also looking for a more reliable supply chain – and Mexico can provide both. And thanks to the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement, which is a free-trade pact between the three nations, companies take advantage to produce products tax free.
Dependency on the appliances sales to the United States
With over 85% exports of appliances to the United States, there is a very high dependency on only one country. If the United States should fall into a recession again, Mexico’s appliance industry would be directly affected. Thus, in the long-term, the country should diversify its client portfolio and take into consideration to produce for other continents such as Europe or Africa as they have the faster supply chain than China.
Electronics
Mexico is one of the main producer of screens, televisions and many other electronic products. There are various key market players like Samsung, LG, GoPro, Dell or Sony with their production places in Mexico. Thanks to the trade agreement USMCA with the United States and Canada, Mexico is the second largest exporter of electronics to the United States and the eight largest manufacturer of electronics overall.
Most manufacturing clusters are in the states of Baja California, Chihuahua and Jalisco.
Some Hard Facts
- 8th largest producer of electronics worldwide
- 5.3% of Mexicos manufacturing GDP comes from electronics
- 150 billion USD annual exports in electronics
- 19 million Samsung TV units in Tijuana
- +500,000 workforce work in electronic
- largest exporter of flatscreen TVs.
- 2,500+ electronic manufacturers
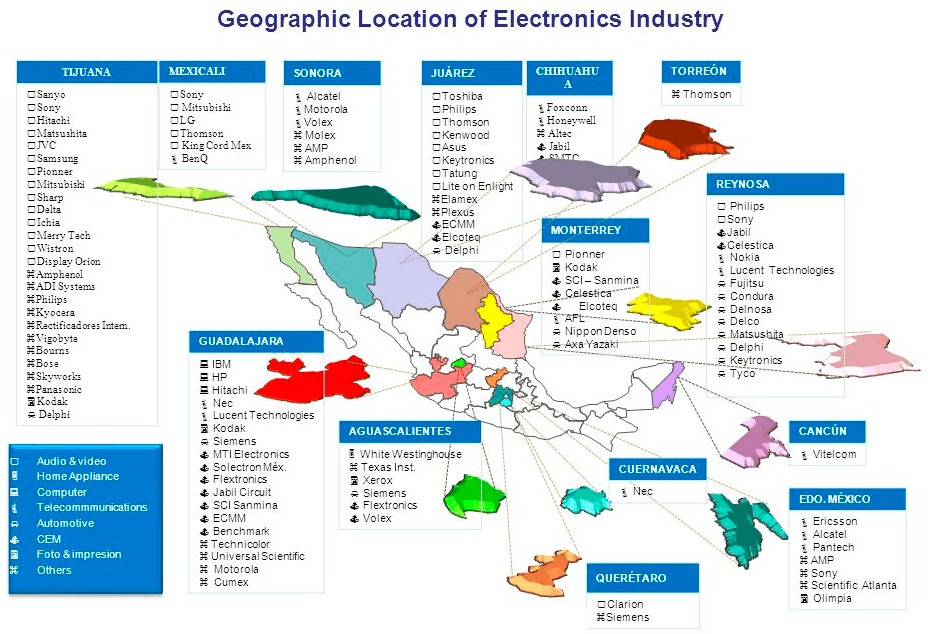
The Electronic Industry in Mexico
Mexico is one of the largest electronic producer worldwide, most produced and exported products are televisions, smartphones and computers. Over the last decades, many of the world’s leading multinational and renowned companies such as LG, Sony, Panasonic, Toshiba or Samsung that comprise the electronics industry in Mexico have established operations in the country. Beside on a mass scale, the country is increasingly specializing in higher value-added products. The industry in Mexico has advanced from a posture of low-mix and high-volume to the manufacture of small quantities of many different products, i.e., low-volume and high-mix.
Since yearly over 100’000 engineering students graduate in Mexico, global manufacturers and suppliers take the advantage to start their operations in Mexico. Based on figures of the Mexico’s National Statistical Directory of Economic Units (DENUE), they have identified more than 1,100 firms that manufacture computer equipment, communication, measurement and other equipment, components, and accessories in the electronics industry in Mexico.
Electronic manufacturing locations
Many of those electronic manufacturing companies are mainly located along Mexico’s borders to the United States as well as central and western regions like Monterrey, Juarez, Guadalajara, or Aguascalientes. They all take advantage cheap labor force and the trade USMCA trade agreement; indeed, Tijuana is one of the largest clusters of electronics manufacturers and assemblers in all of Mexico. However, in contrast to other sectors where the exports are mainly for the United States, Mexico has in the electronic industry a quite diverse clientele. Beside the USA, main export destinations for the consumption of these products are Canada, Colombia, France, and the Netherlands. This demonstrates that Mexico has an extremely successful track record of more than 30 years as an exporter of electronic products. This also due to the reason that Mexico offers trade liberalization throughout the supply and production chains. This means that the country has access to inputs at international prices that are competitive due to the country’s proximity to the highly competitive North American market.
Opportunities with Semiconductor
As mentioned earlier already, Mexico now provides advanced research and design services and the manufacture of highly sophisticated products, including:
- Semiconductors
- Chipsets
- Printed circuit boards
- Microelectronics
- LCD panels
- Microprocessors
As Mexico’s strongest industry – the automotive sector – is very dependent on semiconductors, the trade war and Covid pandemic caused a 20 percent drop in automobile production in Mexico during 2020. During the 10th North American Leaders' Summit held in January 2023 in Mexico, the leaders of Canada, the United States and Mexico, agreed to work on an import substitution plan so as not to depend on Asia for technology, particularly in semiconductors. Indeed, the United States wants to become a manufacturer and not depend on other manufacturers like China or Taiwan for the supply of semiconductors.
Electronic Growth Projections
According to projections by electronics industry analysts, the Mexican exports grew in 2022 more than 4%. The segments with highest export growth have been computer and consumer electronics, and flat-screen televisions, in particular. Beside the OEM who keep investing into their facilities, suppliers to these firms have been also forced to expand to Mexico in order to have a cost-efficient supply-chain. Thus, the pace of new foreign direct investment and new plant openings haven’t stopped – more and more manufacturers are expanding into Mexico than ever before. This has allowed mid-sized and large multinational firms alike to take advantage of Mexico’s beneficial cost structure, logistics, and increasingly qualified labor.
Large electronic investments by Asians
In the coming years, Samsung for example will make significant investments to improve its manufacturing facilities for setting up new chip production. They will invest $500 million into Mexico to boost the production of home appliances, most of it in Queretaro in central Mexico. Samsung already operates a TV assembly plant in Tijuana, Mexico, with an annual output of around 19 million units of plasma, LCD and LED tv’s. Having Mexico has a manufacturing base enables Samsung to effectively cater to the entire North American market.
Over 400 companies from Asia have announced at the end of 2022 to move part of their production outside China to new destinations – to produce close to the United States as well as take advantage from the cheap labor force and the trade agreements. It will undoubtedly have a positive impact on the Mexican economy as transnational companies would seek to bring their production and manufacturing plants closer to Mexico. Beside that the suppliers would take advantage of a much more cost-efficient supply chain, Mexico has the human talent and the material close to the assemblers.
Furniture
As the furniture industry is a very competitive market with low prices and accordingly low margins, many companies’ goal is to have an efficient supply chain and being close to its customers. Thus the demand for more furniture at a cost-effective price is pushing more manufacturers to consider low-cost manufacturing locations.
Mexico is the perfect spot to settle down its productions as the country has already several decades of experience in manufacturing furniture as well as the competitive prices it can offer.
Indeed , Mexico exported $10.675 billion dollars’ worth of furniture in 2017 and there are over 700 furniture manufacturing industry with more than 52,000 employees working in this sector. As an example, The Mexican furniture industry is the third largest exporter of chairs in the world, second only to China and Poland.
Some Hard Facts
- 6%+ growth in 2023
- $10.5 billion export in 2017
- 700+ furniture companies
- 55k+ employees
- 700+ furniture manufacturing companies in Mexico
- $2.5 billion+ exports of furniture to the United States

Furniture Industry in Mexico
Even though Mexico has been manufacturing several years furniture products and it has been a significant sector, the industry has recently grown due to the globalization and the tense relation between China and the United States. Indeed nearshoring has become an increasingly critical strategy for companies seeking to lower their shipping costs or leverage trade agreement benefits that exist between companies near their target sales region. There are several other reasons why Mexico comes to the top of the list of considerations for furniture producers looking to diversify their global footprint.
Thanks to the countries over 50’s international trade agreements, its proximity to the United States as well as to its competitive prices, it is the ideal production place for any furniture company. In numbers, there are over 700 furniture companies based in Mexico, 55k plus employees and there has been over $2.5 billion exports to the United States of furniture products from Mexico.That places Mexico as the fourth largest such exporter behind China, Vietnam and Canada.
USMCA agreement boost relocation
Thanks to the USMCA rule of origin requirements that require portions of miscellaneous furniture products to be manufactured in one of the signatory countries, many companies are moving such manufacturing into Mexico. For example two Chinese furniture companies announcedinvestment projectsin Nuevo León, Mexico, reaching a projected investment of USD $150 million and the creation of more than 1,600 new jobs. Kuka Home, China's largest furniture manufacturer, and Sunon, an office furniture manufacturer, launched new operations in Mexico to meet demand from the North and South American markets. Even though United States is facing a recession in 2023, the Mexican industry will maintain its growth in said market, up to 6% thanks to the nearshoring trend.
Furniture products produced in Mexico
Mexico’s robust furniture industry serves both the international and growing domestic markets and manufacture a wide range of furniture products such as
- Hotel furniture
- Hospitals and veterinary furniture
- Wood and metal furnishings
- Mattresses, beds, bedframes
- Integral kitchens
- Modular bathroom furniture
- Office furniture
- Casino furniture and fixtures
- Seats
- Home furnishings
Who are the largest furniture manufacturers in Mexico?
There are various manufacture furniture companies in Mexico; over 700 national and international companies with a workforce of 55k+ working in this sector. Two years ago, IKEA was choosing to produce furniture in Mexico with its first North American manufacturing plant with over 100,000-square-meter in Saltillo. However, there are many other international brands such as Quetzal, Richer Design, Pottery Barn or Z Gallerie to name a few.
What kind of wood is mexican furniture?
Mexican furniture is crafted from various types of wood, each offering distinct characteristics and aesthetic appeal. Some commonly used woods in Mexican furniture production include cedar, mesquite, and parota. The latter is widely utilized due to its affordability, versatility, and abundant availability in Mexico. Cedar is favored for its natural resistance to insects and durability. Mesquite is known for its rich, unique grain patterns and strength, while parota, a tropical hardwood, is cherished for its stunning grain and sustainable sourcing.
Mexican furniture crafted from these woods can be found in various regions across Mexico, with specific areas renowned for their expertise in woodworking and furniture craftsmanship.
The chart below displays the states and their respective furniture products and tree species of production.
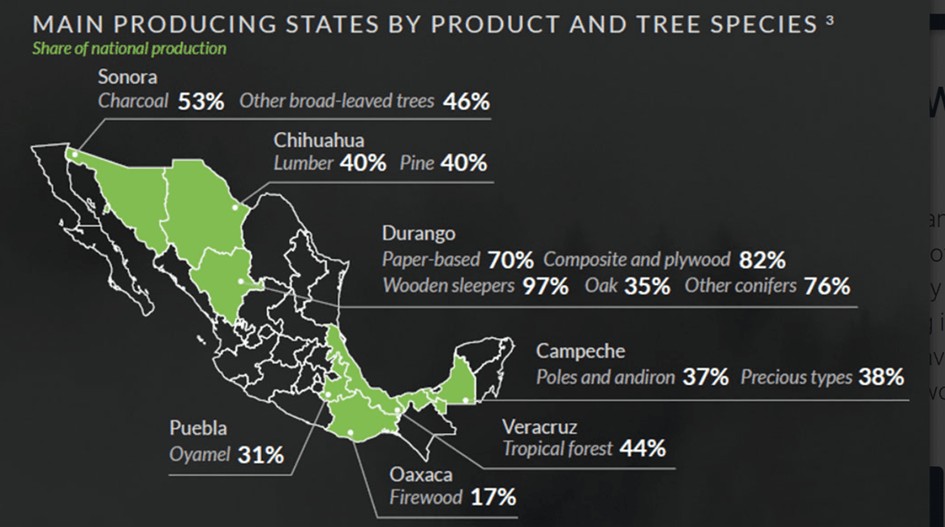
Furniture production locations in Mexico
Mexico's furniture manufacturing production can be found especially in the northern (Nuevo Leon, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Sonora, Baja California) and central states State of Mexico (Jalisco, Puebla).Jalisco for example has become known for its collaboration with the Swedish furniture manufacturing Ikea.
Production in Jalisco's furniture industry with its main spot Guadalajara increased by 9% at the end of 2022, after Mexico gained ground over China as an importer in the U.S. market The manufacturer Palliser Furniture expandedits theater seating and entry-level price furniture in Matamoros, Coahuila. The facility opened in 2017 and put to work new manufacturing methodologies (65,000-square-foot), including the use of conveyor one-piece continuous flow production, to boost its production efficiency and provide more strenuous quality control.Another company named International Furniture Direct expanded its facilitiesin Puebla, southeast of Mexico City, and Guadalajara and doubled its Puebla facility to 280,000 square feet in order to increase production by 50%.
Trends in furniture
Due to the pandemic, the office furnishing trends have been evolving dramatically as many people switch from expansive workstations to flexible workspaces. The largest categories of furniture exports are miscellaneous wood-framed upholstered seats, wood furniture, metal-framed upholstered seats, wood-framed upholstered chairs, and wooden bedroom furniture. In addition, Urban living in the United States and growth in apartment living in Mexico, have increased demand for furniture made to fit smaller spaces.
Medical Devices
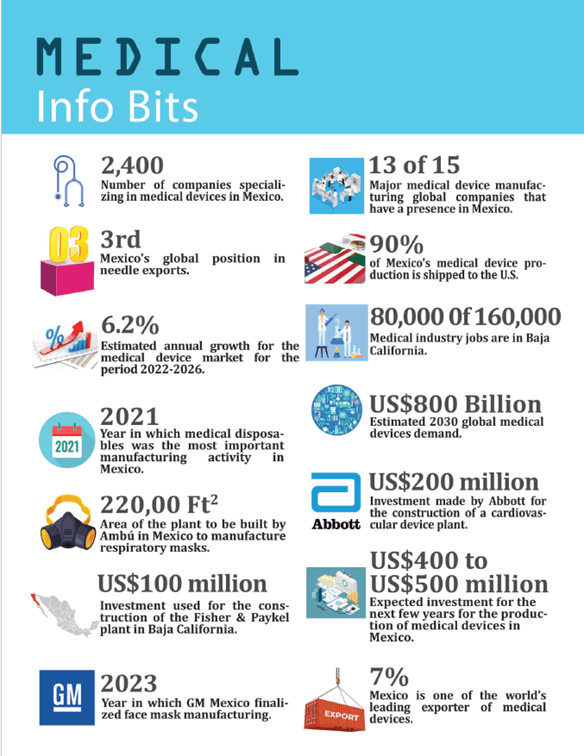
The medical device manufacturing industry in Mexico continues to experience favorable growth. Over the past decades, over 600 medical device manufacturers have leveraged nearshore operations along the U.S./Mexico border regions, which is responsible for having nearly 160,000 workforce and over $9 billion annually in exports.
Mexico is well-known for manufacturing cardiovascular devices, orthopedic devices, and dental devices. One of the greatest benefits of nearshoring medical device manufacturing to Mexico is that the country offers a highly trained and educated workforce.
Some Hard Facts
- 500+ medical device firms in Mexico
- 13 of 15 major medical device companie have presence in Mexico
- 75’000+ employees working in this sector
- $17.6 billion in medical-related products to the U.S in 2023
- 8th largest Medical Device Exporter Worldwide
- 50% of national exports is done by Baja California
- 90% of the medical devices are exported to the United States
Medical Device Industry Mexico
Mexico is emerging as a key player in the global medical device industry, driven by its skilled workforce, competitive costs, and strategic location. Nearshoring has significantly boosted the sector, as medical device manufacturing requires strict quality standards, innovation, and regulatory compliance.
Over recent years, the industry has experienced notable growth, fueled by increasing healthcare demands, advancements in digital health, and personalized medical solutions.
Indeed, Mexico's medical industry has solidified its role as a strategic manufacturing hub, particularly in response to global supply chain disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities in the sector, prompting medical device companies to expand their presence in Mexico to mitigate risks. Nearshoring has emerged as a key strategy, with firms such as BD, J&J, and Medtronic leveraging cross-border operations to ensure stability and efficiency.
With improved U.S.-Mexico relations, supported by the USMCA, Mexico is expected to remain a vital trade partner in the medical device sector, despite some lingering investor uncertainties.
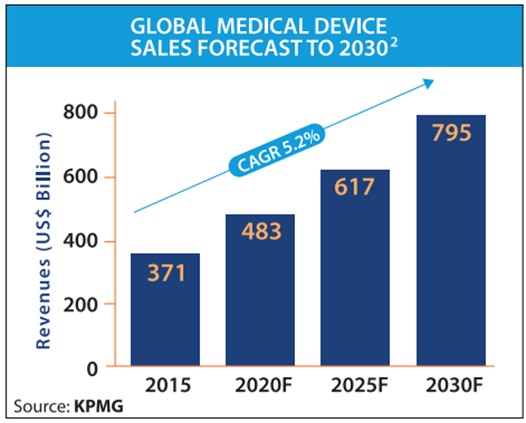
The global medical device market is expected to expand from $540 billion in 2023 to $799.67 billion by 2030, according to CANIFARMA. Mexico itself has seen a 6.7% annual growth in medical device production, with industry leaders projecting that nearshoring could attract at least $500 million in annual foreign investment over the next five years.
The cost efficiency remains as another strong advantage, with lower labor costs and favorable trade agreements offering substantial savings for medical manufacturers. As the global healthcare landscape evolves, Mexico’s role in the medical supply chain continues to grow, positioning the country as a key player in ensuring supply chain resilience and driving innovation in the medical industry.
Medical Device Exports exploded to the U.S
Mexico's medical device industry is experiencing rapid growth and establishing itself as a key global player. With global annual sales expected to exceed $800 billion by 2030, the industry is seeing increased demand for innovative medical devices, such as wearables, and advanced healthcare solutions. Mexico has leveraged its strong manufacturing capabilities, skilled workforce, and strategic location to become with 500+ companies operating in this sector the leading exporter of medical devices in Latin America and the eighth largest worldwide.
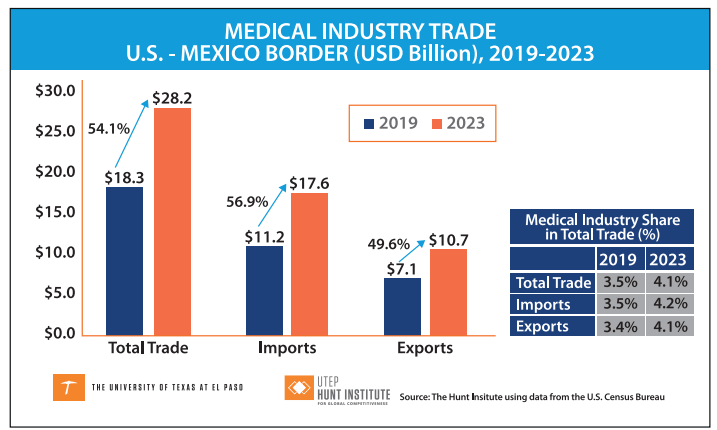
In 2023, Mexico exported US$17.6 billion worth of medical-related products to the U.S., according to the Hunt Institute for Global Competitiveness calculations. However, its contribution to this industry is not limited to medical devices but also medical equipment and Personal Protective Equipment (PPP).
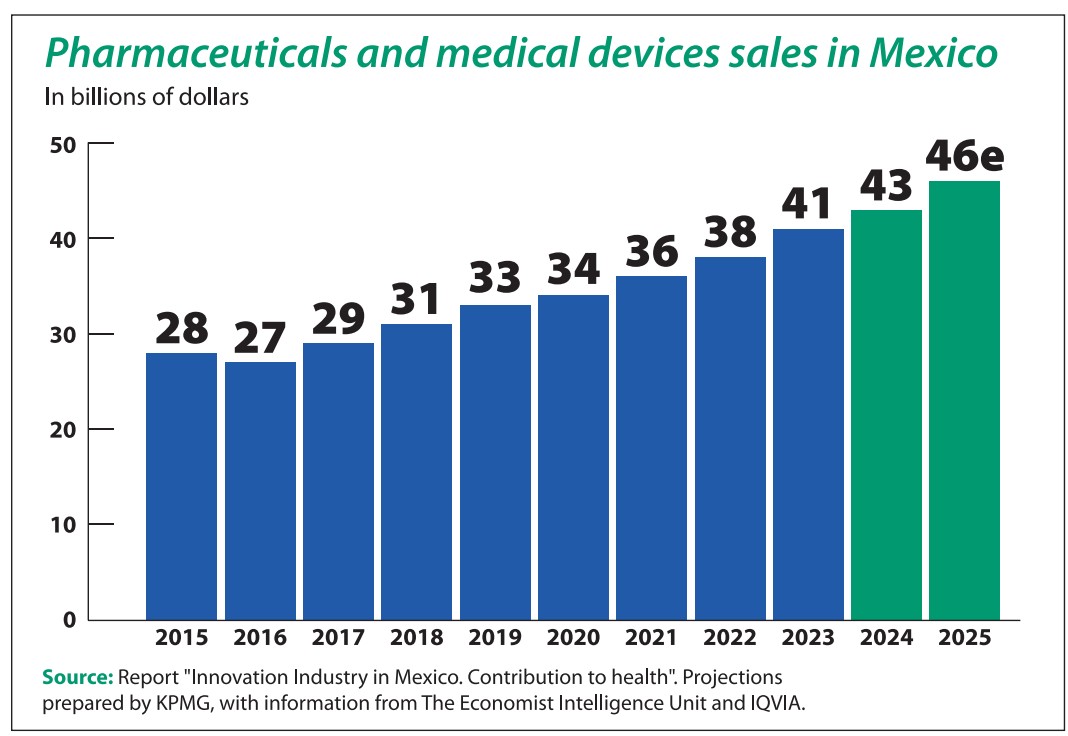
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Device Sales in Mexico
Medical Device Locations in Mexico
Numerous medical device manufacturers strategically position themselves in close proximity to major markets in the United States, facilitating seamless product shipment and exchange. San Diego, California, which is the fourth-largest life sciences hub in the U.S., has a high concentration of medical device manufacturers located in nearby areas.
Baja California as Leader in Medical Device Manufacturing Hub
Hence, key states driving the medical device industry include Baja California, Chihuahua, Nuevo Leon, Jalisco, and Sonora, where major multinational companies and emerging startups are expanding operations. Border cities like Ciudad Juarez and Tijuana play a pivotal role in manufacturing, with significant trade flowing through major ports of entry.
Indeed, Baja California holds the largest concentration of medical manufacturing companies in Mexico and accounts for almost 50% of National Export. The Cali Baja region, for example, houses 353 medical device firms employing over 74,000 people, underscoring Mexico’s role as a powerhouse in medical manufacturing. The state has developed infrastructure and skilled labor force, making it an ideal location for companies to produce medical devices for export to the United States and other markets.
On the other hand, Jalisco is positioning itself as a nearshoring hub, attracting 78 investment intentions from Asian companies looking to relocate production. The state offers strong infrastructure, a business-friendly environment, and a skilled labor force, making it a prime destination for foreign manufacturers.
Medical Device Companies in the whole country
However, as we can extract from the map, the medical device companies are not solely focusing on the border region but have also established themselves in the center of Mexico as well as in the South.
For example, in the Northwest region, Nuevo Leon with the capital Monterrey, Companies in this region benefit from a skilled labor force, access to raw materials, and a favorable business environment. In the state of Jalisco, with its main capital Guadalajara, many companies have established manufacturing facilities in this region due to its skilled labor force, favorable business environment, and proximity to major markets.
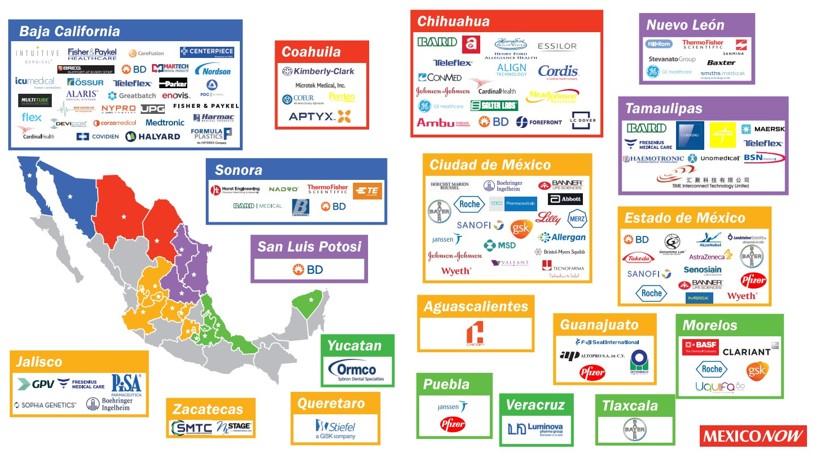
There are various manufacturers that are already in Mexico such as Johnson & Johnson, Philips, GE Medical Systems, Siemens, Medline, Medtronic, Smiths Medical, Abbott Laboratories, or Stryker Corp. They are active in different fields like surgical, dental, orthopedic articles, mechano-therapy applications, veterinary instruments and devices, and surgical furniture, among others.
Companies such as Forefront Medical Technology and Harmac Medical Products are expanding their manufacturing presence in Mexico, recognizing the advantages of reduced logistics costs and faster delivery times.
Joint Ventures in the Medical Device Industry
Joint ventures and acquisitions are also shaping the industry, with companies like TekniPlex acquiring Seisa Medical and Arterex expanding through the acquisition of Micromold. These strategic moves strengthen Mexico's position as an essential hub for medical technology innovation and production. With the presence of global industry leaders such as Medtronic, Jabil, J&J, and Cardinal, Mexico is not only supporting the global healthcare sector but also setting new standards for manufacturing excellence and supply chain resilience.
Additionally, firms like Flexan and ILC Dover are investing in state-of-the-art facilities, obtaining certifications, and enhancing their capabilities to meet the growing demand for high-quality medical devices.
As the industry grapples with supply shortages and cost pressures, companies are increasingly adopting strategic acquisitions and partnerships to enhance resilience and drive innovation.
Main exporter of medical device needles and catheters
Mexico's medical device industry is highly diverse, producing a wide array of essential healthcare products. It ranks as the second largest exporter of tubular metal needles, suture needles, and cannulas, while also manufacturing catheter-based devices, minimally invasive surgical tools, aortic and thoracic stents, diagnostic imaging equipment, surgery kits, respiratory and ophthalmic devices, and infusion pumps.
The country has established itself as a key player in the cardiovascular sector, producing pacemakers, implantable defibrillators, and stents, driven by its precision engineering expertise and proximity to the U.S., the largest market for these devices. Additionally, Mexico is a major manufacturer of orthopedic products, including spinal implants, joint replacements, and trauma fixation devices.
The diagnostic sector is also expanding, with increasing production of imaging equipment, diagnostic tests, and medical devices designed for disease detection and treatment.
Research Centers of Medical Devices
The country's strong research and development capabilities have attracted companies to look to develop new and innovative medical devices. Mexico is also home to several companies involved in the production of dental devices, including orthodontic appliances, dental implants, and prosthetics. The country's skilled labor force, low production costs, and strategic location have made it an attractive location for companies looking to expand their dental device operations.
Factors of the medical device growth in Mexico
The growing demand for medical products—driven by an aging population, rising chronic diseases, and increased healthcare needs—has fueled the expansion of Mexico’s medical manufacturing ecosystem. The country benefits from an extensive supply chain network, offering access to raw materials and specialized service providers. However, sterilization remains a significant challenge for medical-related companies, along with navigating the complex regulatory landscape.
The pharmaceutical sector presents significant opportunities for Mexico to expand its footprint in the U.S. market, addressing critical drug shortages. Despite its high manufacturing standards, Mexico’s pharmaceutical exports remain modest compared to dominant players like China and India. However, the need for diversification in global supply chains presents Mexico with an opportunity to become a more significant supplier of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and essential medicines.
Government Incentives in the Medical Device Sector
In addition, the Mexican government has implemented policies to support the growth of the medical device industry, including tax incentives, research and development grants, and streamlined regulatory processes. These factors have made Mexico an attractive location for companies looking to expand their medical device operations and tap into the growing demand for medical devices in the global market.
Complex Medical Device Guidelines & Regulations
Recent changes by COFEPRIS in 2024 aim to streamline medical device approvals, expediting market entry. Additionally, the Mexican government has introduced tax incentives to encourage nearshoring, including accelerated depreciation for machinery and additional tax deductions for employee training, further strengthening Mexico’s appeal as a manufacturing destination.
Mexico enforces rigorous guidelines and regulations governing the manufacturing of medical devices. Companies are required to comply with strict regulations and standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. These regulations cover all aspects of the manufacturing process, from design and development to testing, production, and distribution. Compliance with the Mexican Official Standard (NOM) for medical devices is mandatory, incorporating criteria for risk management, quality assurance, and product labeling.
In addition to the NOM, the manufacturers must also comply with international standards such as ISO 14971:2019, which outlines requirements for risk management and ISO 13485:2016, which outlines requirements for the quality management system of medical device manufacturers.
COFEPRIS Mexico
The regulatory body responsible for overseeing the medical device industry in Mexico is the Federal Commission for the Protection Against Sanitary Risk (COFEPRIS), which operates under the Ministry of Health. Manufacturers are required to secure certifications and approvals from COFEPRIS to legally market and distribute their products within Mexico. These include obtaining a Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) or a Certificate of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for exporting the products to other countries.
Overall, Mexico's regulatory framework for medical devices is rigorous and designed to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices manufactured in the country. This helps to ensure that patients receive high-quality medical devices that meet international standards.
Technological Trends in the Medical Device Industry
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping medical manufacturing in Mexico. Artificial intelligence, telemedicine, Big Data, IoT, surgical robotics, synthetic biology, and genomic medicine are some of the key trends driving innovation. Digitalization and automation have become critical for companies looking to stay competitive in the global market.
GE Healthcare, for example, invests $1 billion annually in research and development, holding more than 11,000 patents. This level of innovation is expected to further accelerate the capabilities of Mexico’s medical device sector, making it more attractive for foreign investment and nearshoring opportunities.
Mexico is currently the fifth-largest exporter of medical devices in the world, supplying 20% of all medical equipment imports to the United States. If the country continues investing in infrastructure, energy capacity, and regulatory efficiency, it has the potential to move up in global rankings. Industry leaders believe that with strong collaboration between government, academia, and private companies, Mexico can solidify its role as a leading global hub for medical device manufacturing and innovation.
Key Benefits of Medical Device Nearshoring
- Faster access to advanced medical equipment – Diagnostic and surgical devices that previously required long import times from Europe and Asia are now more readily available.
- Lower operational costs – Mexico’s geographic proximity allows for more efficient logistics, reducing transportation expenses and making medical technology more affordable.
- Increased foreign direct investment in healthcare infrastructure – New capital is strengthening the country’s hospital network, improving access to modern medical technologies.
Despite its rapid growth, the industry faces several challenges, particularly in logistics and regulatory processes. The supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities, such as shipping delays, container shortages, and rising costs. Companies are now focused on strengthening supply chain resilience to ensure a more stable production and distribution network.
Sanitary Registration and Certifications
Regulatory bottlenecks remain a significant issue, with delays in obtaining sanitary registrations and certifications slowing down the market entry of new medical devices. While Mexico has made progress in streamlining regulatory processes, industry experts emphasize the need for faster approval procedures to accommodate growing demand. Another key challenge is technology transfer and the promotion of Mexican-branded products. Many companies still rely on imported technologies rather than developing domestic brands, limiting the sector’s potential for innovation and economic growth.
Information Technology
The information technology (IT) industry in Mexico has experienced significant growth in recent years. It is one of the largest in Latin America, with an estimated value of $48 billion in 2021, according to the Mexican Association of Information Technology Companies
The sector encompasses several sub-sectors, including IT services, hardware manufacturing, software development, and e-commerce. Software development is the largest sub-sector, accounting for around 60% of the industry's value.
In addition, the country has become an attractive destination for foreign investment in the IT industry, with several multinational companies establishing a presence in the country.
Some Hard Facts
- 110k+ engineering graduates per year
- 3rd largest IT exporter in the world
- 21 billion in exports
- 40+ IT clusters

Information Technology in Mexico
Mexico’s information technology (IT) sector is well established and belongs to the top 3 for offshoring options with the tech industry which is expanding at 3x the global average. Indeed, the industry is pulling more than US$12 billion a year with more than 4,000 companies across the country contributing to the sector. Some companies are IBM, Oracle, Softtek, or Intel. Factors for the rapid growth are Mexico’s strategic location, skilled workforce, favorable business environment, and government support. Also, Mexico also has a favorable time zone that allows companies to provide 24/7 services to clients in North America.
Beside call centers, Mexican IT industry offers a range of services, including software development, data analytics, cybersecurity, IT consulting, and digital marketing. And due to the investment of the Mexican government and growing infrastructure, more development talent is emerging in Mexico at lower salary rates than their American counterparts; graduates in Mexico earn four times less than people from the United States who do not even have a degree.
There are different information technology provided such as cloud computing, data analytics, digital transformation, cloud services, cybersecurity, application development, and digital transformation. Thus, it is not surprisingly that the Information Technology sector in Mexico is also positioned as a high-quality software developer, benefiting the needs of aerospace manufacturing as well as financial industries.
Growing IT Mexico
The Mexican IT industry is one of the fastest-growing in the region, with an annual growth rate of around 12%. According to the Mexican Association of the Information Technology Industry (AMITI), the industry's revenue was $38.3 billion in 2020, and it is expected to reach $50 billion by 2025.
The country has a large pool of skilled IT professionals, with around 650,000 people employed in the IT sector. More than 130 universities and technical schools offering IT-related courses and programs, producing around 120,000 graduates in the field each year, which represents over 20% of all the graduates. The government has also established technology parks and innovation centers to encourage collaboration and innovation in the industry.
Tech hubs in Mexico
Major IT industrial sectors are in the capital Mexico City, Guadalajara and Monterrey, whereas the state Jalisco is the home for 40 percent of Mexico’s IT industry and a well-educated workforce. Indeed, Guadalajara is being called the Silicon Valley of Latin America. Jalisco – Latin Americas most important innovation hub – goal is surpassing US$5 billion in Foreign Direct Investment, generating more than 80,000 jobs in the sector and reaching US$50 billion in exports by 2030.
Furthermore, there are 16 technology institutes and 12 universities with more than 8,000 technical and engineering students graduating every year from the state. The government has made the software sector a priority and has established the Program for the Development of the Software Industry (PROSOFT) initiative. Through the initiative, the Mexican government wants to reach a production level of 5 billion dollar of software development and become a leader in Latin America.
Data Centers in Mexico
In the last years, there’s been a quickly growing need for data center infrastructures, cloud computing, and security services, as well as business intelligence software to keep pace with market demand. According to a report by Datacenter Dynamics, the market was valued at $1.2 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $2 billion by 2025, which means an annual growth of 10%.
The countries’ favorable location makes it an attractive location for data center operators looking to serve both North American and Latin American markets. The proximity to the United States also makes it an ideal location for disaster recovery and backup facilities. Several major data center operators have established a presence in Mexico, including Digital Realty, Equinix, and KIO Networks. These companies operate data centers in several Mexican cities, including Mexico City, Monterrey and Queretaro. Indeed, Queretaro has become the primary data center hub and contributes to over 65% of the data center facilities in Mexico. As those data center operators need lots of energy, building renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power to reduce their carbon footprint and lower operating costs, this should be one’s of the governments primary goal.
IT-Exports mainly to the United States
Many of these IT companies in Mexico export their products and services to other countries worldwide, including the United States, Canada, and Europe. The United States is the largest market for Mexican IT exports, accounting for around 85% of the country's IT exports. Other significant export destinations for Mexican IT companies include Canada, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Japan.
Raw Material
Mexico’s favorable business environment and diverse economy make it an attractive location for companies looking to source raw materials or set up manufacturing operations.
The country is rich if not abundant of raw materials such as oil and petroleum products to mining, coal, silver, gold copper, zinc, minerals, automotive parts, agriculture, electronics, textiles, chemicals, plastics, and electrical equipment.
Some Hard Facts
- world’s largest producer of silver
- 2.5 million work in the mining industry
- 45.4 B cu m of natural gas production in 2017
- 11th largest oil producer worldwide
Various Raw Materials production Mexico
Mexico is a country with a rich and diverse supply of raw materials that make it an attractive destination for foreign investors. It is one of the largest oil producers in the world and has a lot of reserves of oil and natural gas. Behind the USA, Canada and Venezuela, Mexico is the world’s 11th largest oil producer, 13th largest oil exporter, with the 17th largest oil reserves, and 4th largest producer in the Western Hemisphere.
In addition, the country is also a major producer of agricultural products, including wheat corn, sorghum, tomatoes, beans, and soybeans among others. Thanks to its stable political system, favorable business environment, skilled workforce, and proximity to the United States and other major markets make it an ideal location for foreign companies looking to tap into the country's vast natural resources. The raw material is one of the reasons why many foreign investors explore investment opportunities in this dynamic and growing economy.
Plastic production in Mexico
As Mexico is an attractive location for manufacturers from various industries, the country produce for different sectors, including packaging, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. It has experienced steady growth in plastic production over the years; in 2021, it was producing around 7.3 million metric tons of plastic annually, making it one of the largest plastic producers in Latin America. And the growth will stay thanks to the nearshoring trend.
Mexico is a major producer of automotive parts and components, with many international automotive companies operating manufacturing facilities in the country. Various manufacturing clusters are well known for their plastic manufacturing facilities states such as Nuevo León, Coahuila, and Mexico City. Thanks to the reason that more and more manufacturing companies relocating from China to Mexico, the plastic plays a crucial role for the automotive industry. The automotive industry use plastic components like bumpers, interior parts, dashboards, and fuel tanks due to their lightweight, durability, and design flexibility.
Also, the packaging is a significant application for plastics in Mexico. It is used in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, personal care products, and consumer goods. Plastic packaging provides convenience, durability, and protection for products. Lastly, Mexico has a lot of refineries and petrochemical complexes that produce the raw materials needed for plastic manufacturing, including ethylene and propylene, which are derived from petroleum and natural gas.
A significant amount of the plastic products are exported to international markets, particularly to the United States.
The mining industry
Mexico is the largest silver producer world wide. The silver is used for the trending products electric cars, solar panels and 5G telekom networks. TheZacatecas is one of the most important mining states in Mexico, and its attractiveness to the mining industry. The state is home to significant mineral reserves, including gold, silver, zinc, copper, lead, and, among others. Indeed, Zacatecas is the leading producer of silver in Mexico and one of the largest in the world in this sector. The city has a very strong infrastructure, including roads, railways, and ports, that facilitates the transportation of minerals and mining equipment. Over 70% of total exploration investment in the Mexican mining industry is made by foreign companies; however, 60% of the total production value is generated by Mexican companies. Canada represents over 70% of the total foreign investment related to the mining sector in Mexico.
Thanks to favorable with laws and regulations, it promotes foreign investment and protect mining assets. The government has implemented policies to encourage mining investment and streamline the permitting process.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Mexico is a major player in the assembly manufacturing industry, with a focus on automotive, electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods production. Thanks to the reason that Mexico has raw materials such as steel, aluminum, plastics, and electronic components are utilized in manufacturing and assembly processes. Beside the automotive, the electronic industry with products such televisions, computers, and home appliances will grow fast thanks to the nearshoring trend.




