Mexico the country
Mexico is not just the country of Tequila, Sombreros and Tacos, but enjoys the reputation of having a strong manufacturing export sectors, commerce, and service industry. The strategic location, educated workforce, competitive labor costs, and advanced cross-border infrastructure, position the country as a premier investment hub.
Some Hard Facts
- 131 million (Mexico City, 25m)
- Size: 1,972,550 square km Size (5 ½ as big as Germany)
- BIP 2023: 1.788,8 Billion USD / 13’600 USD per head
- 13 Trade Agreements with 52 states (Nafta, EU, Pacific, Sela, Aladi, WTO, IMF
- 12th biggest economy worldwide
- 17th place for tourists worldwide
- Currency: Pesos (1 Dollar = 1.2 Peso)
- Average age 29 years
- Average wage: $700 dollars / month
Mexico the new China
China emerged as a global manufacturing hub due to its low labor costs, driven by a large and young workforce, government support through incentives and subsidies, and robust infrastructure like efficient ports and modern airports. In addition, its technological advancements further strengthened its position, enabling leadership in developing cutting-edge manufacturing technologies. While businesses benefited from reduced expenses and efficiency, challenges such as quality control, intellectual property risks, and political instability remain.
Though in the last years, Mexico has become an increasingly popular option for businesses looking to start its manufacturing base. This is thanks to its open borders and trade policies as well as the similar time zones.The nations’proximity to the United Statesprovides companies with a large market for exporting its products and services, especially in manufacturing.
Nearshore to Mexico
In addition, due to recent events like the pandemic, the broken supply chain (sea freight blocked the river and Houthi-Attacks), the Ukraine War, or thetense relation between the United States and China, many companies must overthink their strategy and diversify their portfolio. The concept of “reshoring” took off in China after the trade war with US in 2018 started. Tariffs on billions of dollars’ worth of Chinese goods led investors to reconsider the viability of China as a destination for manufacturing and other operations.
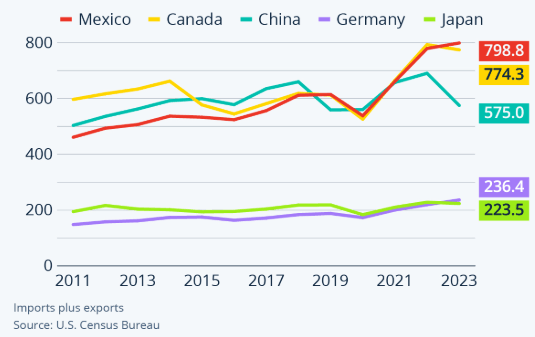
Hence, over the past five years, the landscape of U.S. imports has shifted dramatically, with Mexico and Canada overtaking China as the top suppliers. China's contribution to U.S. imports declined to 13.35%, while Mexico and Canada captured 16% and 15% shares, respectively. In 2023, Mexico's exports reached approximately $799 billion USD, outpacing Canada at $774 billion and China at $575 billion USD.
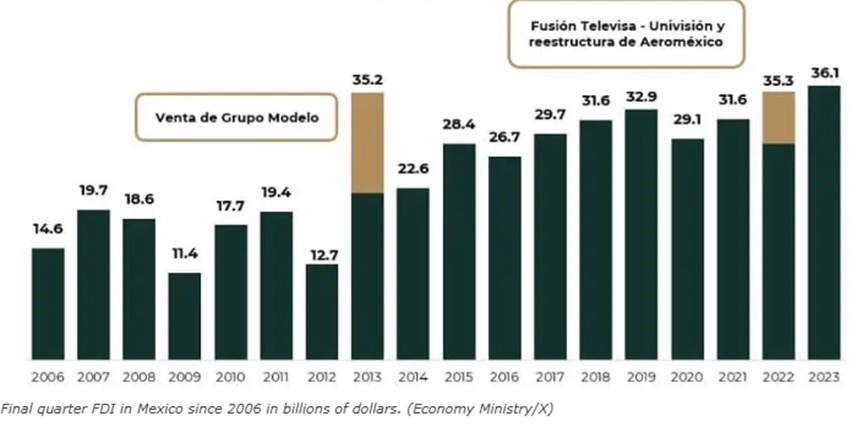
Record Foreign Direct Investments in 2022 and 2023
From 2006 to 2023, FDI inflows have generally increased, reflecting Mexico's growing attractiveness as a manufacturing hub, its strong trade agreements (such as the USMCA), and its strategic position as a nearshoring destination for companies looking to diversify supply chains.
Mexico's FDI has demonstrated a consistent upward trajectory, with manufacturing receiving the largest share of investments. The 2023 FDI of $36.06 billion marks a 2.2% increase from the previous year and is the highest preliminary total ever recorded.
Investments until 2030
Even though there are challenges of corruption or security issues, Mexico has developed itself as a stable economy and political situation, allowing businesses to build long-term relationships and protect their investments. The Mexican government has taken steps to improve the business environment and attract foreign investment, including implementing economic reforms and promoting investment in key sectors such as energy and infrastructure.
Sheinbaums Plan
Mexicans new President Claudia Sheinbaum unveiled her administration’s strategy to position Mexico among the world’s top 10 economies by 2030. Currently ranked 12th, Mexico plans to achieve this by boosting local manufacturing, reducing reliance on imports, cutting bureaucracy, and attracting investment.
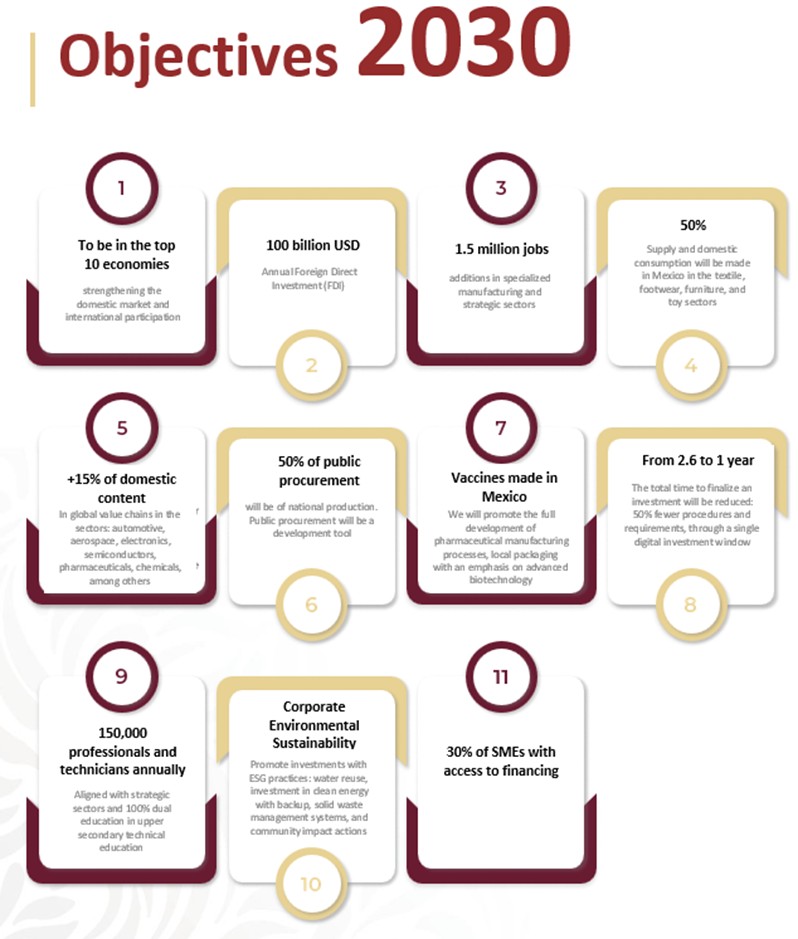
Key goals include increasing investment to 28% of GDP, creating 1.5 million manufacturing jobs, and strengthening local sourcing in industries heavily dependent on Chinese imports, such as textiles and automotive. Mexico also aims to enhance trade agreements, enforce customs policies, and address trade tensions with the U.S., particularly regarding accusations of enabling Chinese goods to bypass tariffs.
Sheinbaum’s administration emphasizes collaboration with private-sector partners and aims to transition Mexico’s energy grid to 45% sustainable energy, though challenges remain with the state oil firm Pemex. Ultimately, Sheinbaum’s plan prioritizes reducing poverty, inequality, and creating a more robust, sustainable economy.
Energy Investments
President Sheinbaum's administration is set to prioritize substantial investments in Mexico's energy infrastructure over the coming years, with a focus on sustainability and modernization.
A total of $23.4 billion USD will be allocated to the generation, transmission, and distribution of energy, including $13.6 billion USD dedicated to the construction of new power plants. These initiatives aim to enhance the country’s energy capacity while aligning with environmental goals, as 45% of Mexico's electricity grid is projected to rely on renewable energy sources.
Water Investments
Under the new administration, a significant focus will be placed on water management and sustainability projects. By 2025, the government plans to invest 20 billion pesos in public projects aimed at water sanitation and the restoration of key water bodies, including the Lerma-Santiago, Atoyac, and Tula rivers.
Public Infrastructure
In recent years, Mexico has significantly expanded and reoriented its public infrastructure investment. Following a period of reduced spending during the pandemic, the government has prioritized projects that promote economic growth, reduce inequality, and enhance national connectivity.
A substantial share of these investments includes the development of over 3,000 kilometers of railways dedicated to passenger and cargo transport, marking a significant boost to Mexico's connectivity and logistics. Additionally, investments will focus on enhancing urban mobility infrastructure, aiming to improve public transportation systems and reduce congestion in cities.
Challenges & Risks
Mexico faces challenges in energy and water scarcity, security, infrastructure, and the political landscape. To effectively address these risks and harness Mexico’s potential, companies should adopt a proactive strategy that includes comprehensive planning as well as collaborating with reliable partners and experts with specialized knowledge in these areas to ensure informed decision-making and effective risk mitigation.
Energy Scarcity
Mexico's reliance on natural gas, which accounts for over half of its energy mix, combined with aging infrastructure, makes the system vulnerable to supply disruptions and price fluctuations. This is particularly evident in the northern and central regions, where frequent power outages disrupt industrial activity.
To face these challenges, companies should undergo a feasibility study how much energy will be needed and then prioritize operating in areas with reliable energy capacity, ensuring legal agreements guarantee sufficient energy availability, especially for energy-intensive operations. Conducting feasibility studies to assess energy infrastructure and supply reliability is crucial for high-consumption projects.
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity poses a major obstacle to industrial development in Mexico, particularly in the northern and central regions like Nuevo León and Guanajuato. To address this challenge, companies should carefully evaluate water availability during site selection to align with operational needs. Adopting water-efficient strategies, such as recycling water in industrial processes, rainwater harvesting, and investing in advanced water treatment technologies, is essential.
Security
Cargo transportation in Mexico faces significant risks from robberies, leading to potential financial losses and operational disruptions. These risks depend on the geographic region, local security conditions, and the type of cargo being transported. In the site selection process, it is vital that leveraging local expertise is critical to identify secure routes and optimize supply chains. Collaborating with carriers and authorities to ensure that the highways with tolls will be used and the trucks are equipped with GPS technology, which improves tracking and operational control. Additionally, comprehensive insurance coverage is essential to protect against unexpected losses or damages.
Renegotiation USMCA
One of the main concerns for international companies considering expansion to Mexico is the upcoming 2026 review and potential renegotiation of the USMCA, which creates uncertainty. If President Trump were to increase tariffs by 25%, it could significantly disrupt North American trade flows. To navigate this, it is crucial for companies to stay informed by gathering insights through local chambers of commerce and government sources. This proactive approach will help businesses anticipate potential challenges and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Hard Facts Country
- BIP 2019: 1,3 Mrd. USD / 9860 USD pro Kopf
- 11th most populous country in the world.
- 13 Trade Agreements with 52 states (Nafta, EU, Pacific, Sela, Aladi, WTO, IMF)
- Currency: Peso
- Major Industries: food and beverages, tobacco, chemicals, iron and steel, petroleum, mining, textiles, clothing, motor vehicles, consumer durables, tourism Agricultural Products: corn, wheat, soybeans, rice, beans, cotton, coffee, fruit, tomatoes; beef, poultry, dairy products; wood products Natural Resources: petroleum, silver, copper, gold, lead, zinc, natural gas, timber
- Major Exports: manufactured goods, oil and oil products, silver, fruits, vegetables, coffee, cotton
- Major Imports: metalworking machines, steel mill products, agricultural machinery, electrical equipment, car parts for assembly, repair parts for motor vehicles, aircraft, and aircraft parts
- Natural resources found in Mexico include antimony, copper, gold, lead, natural gas, petroleum, silver, timber, and zinc.
Geographical facts Mexico
- The capital is Mexico City.
- Population 126,000,000. Yearly increasment ca. 1,2 %
- Major Cities; Mexico City 25(M), Guadalajara (7M) and Monterrey 6M).
- About 25% of the population lives in or near Mexico City. The middle of the country is the most populated. Most Mexicans live between the states of Jalisco and Veracruz.
- Size: 1,972,550 square km Size (5 ½ as bi gas Germany)
- Age structure2016: 0-14 years: 27%; 15-24 years: 18%; 25-54 years: 41%; 55-64 years: 7%; 65 years und older: 7%
- Climate: varies from tropical to desert
- Mexico faces natural hazards including tsunamis, hurricanes, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
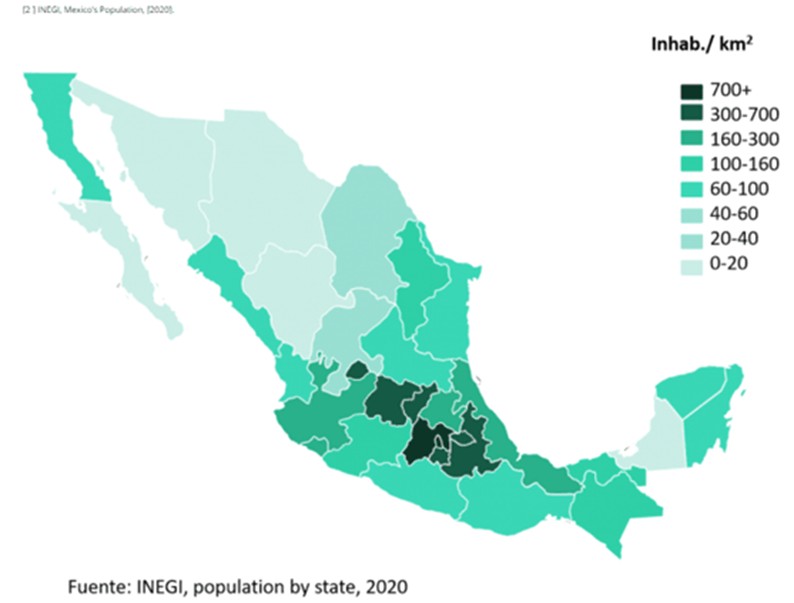
Population of Mexico
Geographically, the population is located mainly in the central region of the country and around Mexico City metropolitan area, heart of the country’s political and financial activities. The most populated metropolitan areas are:
- Mexico City (20,892,724 inhab.)
- Guadalajara, Jalisco (4,887,383 inhab.)
- Monterrey, Nuevo Leon (4,689,601 inhab.)
- Puebla, Puebla (2,941,988 inhab.)
- Toluca, Estado de Mexico (2,202,866 inhab.)
Culture of Mexico
Mexican culture is influenced by the rich history of its native peoples, the Spanish who ruled the country for three centuries. But not only, the country has a strong cultural affinity with the United States, particularly due to its long history of collaboration and exchange in culture, education and business. This makes it easier for businesses to collaborate and exchange with their nearshore partners, leading to smooth operations and effective teamwork.
Apart from art, Mexicans have a long history and tradition of sports. An ancient ball game was played in Mexico centuries ago, and back then, the losers were sometimes killed. Today, competitors in bullfighting and rodeo still endanger their lives while engaging in sports, but the most popular sports in Mexico are ones that are common in other countries, too, like soccer and baseball.




