Nearshoring-Boom
Mexico has been known since decades as a manufacturing country. However, the Covid-19, Ukraine War, the U.S.-China trade conflict, the Houthy Attacks, and general supply chain vulnerabilities have brought significant international challenges, disrupted global supply chains and driving companies to seek more reliable regional partners.
These factors, combined with growing investments, a strong manufacturing sector, and modernizing infrastructure, solidify Mexico's position as a premier destination for companies looking to relocate or expand operations.
The Global Conflicts
Trade War USA - China
The US-China trade war, initiated in 2018 under President Trump, aimed to address concerns over trade imbalances, intellectual property theft, and China's protectionist policies. With tariffs imposed on billions of dollars in goods, the conflict disrupted global trade and led companies to reassess their supply chains. Mexico emerged as a prime beneficiary due to its geographic proximity to the US, competitive costs, and the favorable terms of the USMCA agreement.
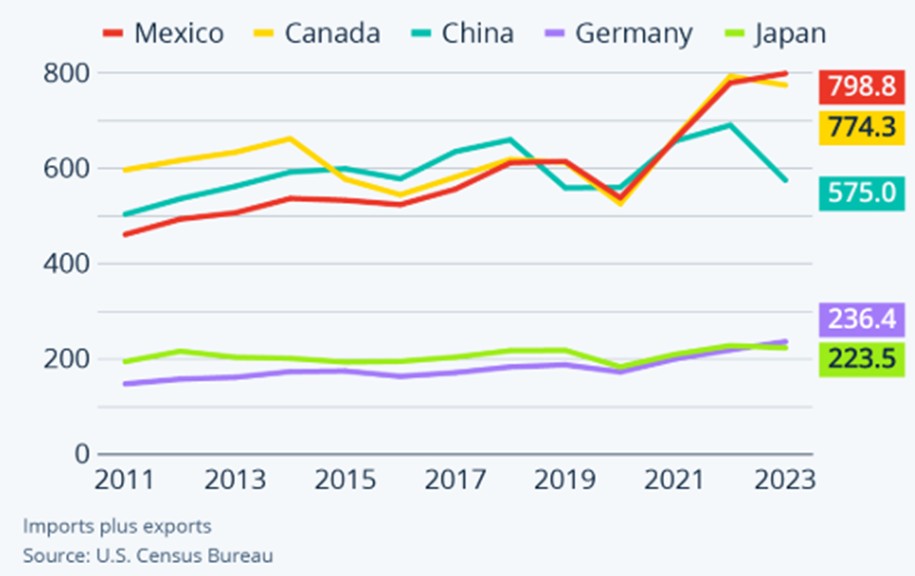
Leading Trading Partner – before China
Indeed Mexico has surpassed China as the leading trade partner of the United States in 2023, marking a significant geopolitical and economic shift. While Mexico’s exports to the US grew by 4.6%, Chinese exports dropped by 20%, reversing a decades-long trend. Despite NAFTA’s 1994 promise of making Mexico a dominant US trade partner, China’s entry into the WTO in 2001, along with lower wages and currency policies, propelled it ahead until now.
Three key factors contributed to Mexico’s rise:
- Geopolitical Tensions – US tariffs on Chinese imports, initiated under Trump and continued under Biden, have pushed companies to seek alternative suppliers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions – The COVID-19 pandemic exposed risks in long-distance supply chains, accelerating nearshoring trends.
- Rising Chinese Wages – Higher wages in China have made Mexican manufacturing more competitive.
As US-China relations remain strained, with potential for further tariffs and regulatory measures, Mexico continues to attract businesses seeking alternatives to Chinese manufacturing. The 2026 USMCA review could further strengthen Mexico's role as a nearshoring hub, bolstering its manufacturing and export capabilities and cementing its position in global supply chains.
Russia - Ukraine War
The Russian invasion, driven by geopolitical tensions and territorial ambitions, began in early 2022. The conflict continues to result in significant humanitarian impacts and military struggles, with no certainty of a resolution or stability in the region in the coming years. The unstable situation in Ukraine and Russia has led many international companies to relocate their production from the region. Maquiladoras, which were responsible for manufacturing mass-produced goods in these countries, are facing significant challenges; the uncertainty and geopolitical tensions are driving companies to seek alternative locations to secure their supply chains and minimize risks.
Increasing Energy Prices affect Europe Companies
Europe's energy crisis in 2022 exposed its heavy reliance on Russian fossil fuels, with about 45% of its gas, 25% of its oil, and 45% of its coal imports coming from Russia. This dependency developed over decades and became critical during geopolitical conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war. Despite warnings from past disputes, Europe failed to diversify its energy sources in time.
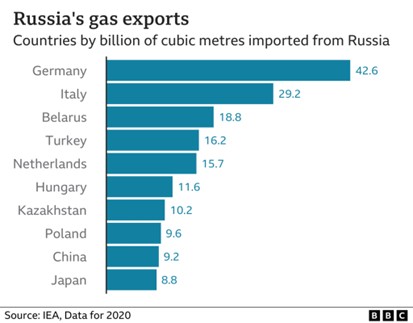
As we can see on the graph, Germany, Europe's leading manufacturing country, is heavily dependent on Russia for energy. After sanctions were imposed, an energy crisis ensued, significantly impacting its economy and resulting in higher energy costs and economic contraction. They are importing more electricity than ever, with 5,783.4 gigawatt-hours in July 2023, setting a new record.
This has not only had a negative effect on private households but has also led to high energy costs that have affected German industries. The automotive sector, for example, faces significant adaptation challenges to electric vehicles, which could lead to potential job cuts. Hence, the energy crisis has led to higher energy costs, economic contraction, and challenges for German industries, underscoring the need for strategic energy policies and economic reforms.
Dependency on Russian Gas
To address the crisis, the EU launched initiatives to reduce Russian gas imports by two-thirds in 2022 and to eliminate reliance on Russian fossil fuels by 2030. However, high energy prices and long-term contracts in the LNG market complicated the transition. Many European countries, still reliant on Russian gas, struggle to produce enough sustainable, clean energy.
Mexico as an Alternative
Due to the disruptions in global supply chains and sanctions on Russia have impacted commodity prices, including oil and gas, could be in favor of Mexico's economy. Indeed, as the outcome of the conflict remains uncertain, with potential paths ranging from prolonged fighting to diplomatic resolutions. The resolution will have major implications for global energy markets, trade relations, and international alliances.
Mexico, with its stable political environment and favorable production conditions, is increasingly seen as an attractive alternative for businesses looking for secure and efficient manufacturing solutions.
Houthi Attacks in Suez Canal
In addition to the 2019 Suez Canal blockage caused by the Ever Given, which resulted in a $55 billion loss in just days, the increase in Houthi rebel attacks in 2023 in the Red Sea has further disrupted global supply chains, particularly impacting shipping traffic between Asia and Europe through the Suez Canal. These drone and missile attacks, fueled by the ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict, have targeted various commercial vessels.
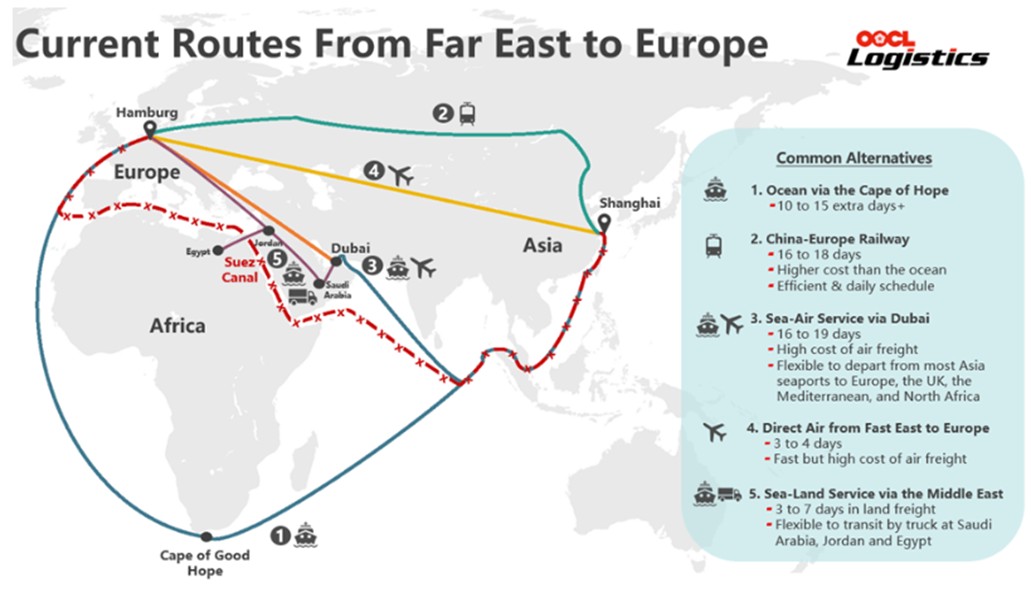 As a result, major shipping companies, including Maersk, have opted to reroute around Africa, leading to significant delays and higher shipping costs.The re-routed route (blue line) around the Cape of Good Hope vs. the Suez Canal (red line) adds up to two weeks to delivery times, costing over $1 million extra in transportation expenses.
As a result, major shipping companies, including Maersk, have opted to reroute around Africa, leading to significant delays and higher shipping costs.The re-routed route (blue line) around the Cape of Good Hope vs. the Suez Canal (red line) adds up to two weeks to delivery times, costing over $1 million extra in transportation expenses.
Panama Canal Crisis
The Panama Canal is a vital global trade route, linking the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and saving ships thousands of miles in travel. Over two-thirds of cargo passing through originates from or is destined for the U.S., making it a strategic asset for American trade.
While China has economic interests in Panama, the canal remains under the control of the Panama Canal Authority. Former U.S. President Donald Trump has raised concerns over Chinese influence and Panama’s toll policies, sparking diplomatic tensions.
Interoceanic Corridor as an alternative
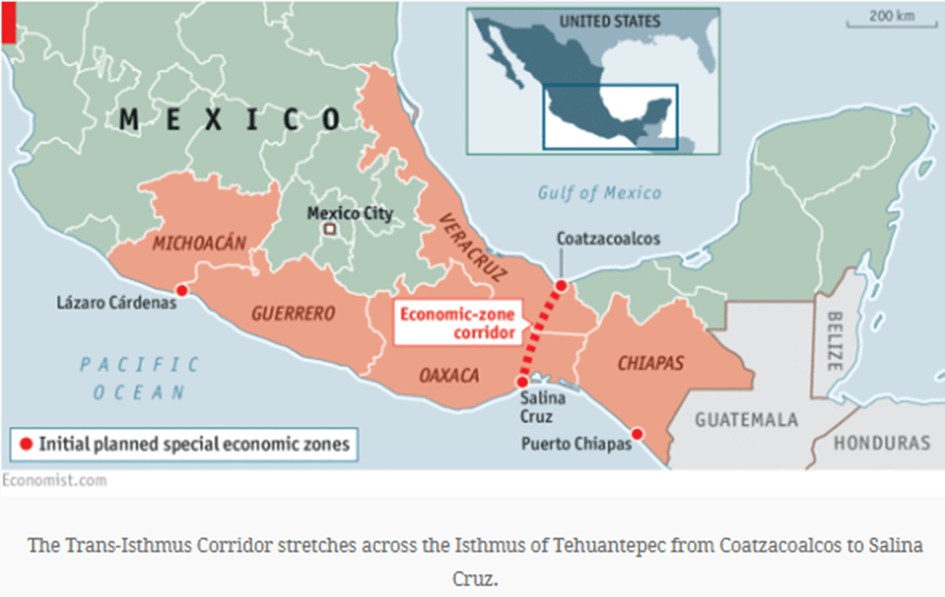
This conflict strengthens Mexico's position as a global logistics hub, with the Interoceanic Corridor emerging as a strategic alternative to the Panama Canal, helping to mitigate trade disruptions and enhance Mexico's role in international shipping.
Ineed, the Interoceanic Corridor is an ambitious infrastructure project in Mexico designed to connect the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans through a multi-modal logistics platform. The corridor is what technicians call a dry canal, a corridor with 309 km railways infrastructure for freight trains and a road with a highway in certain sections as well as two ports, with a focus on enhancing the economy of southern regions, particularly Veracruz and Oaxaca.
It is anticipated to facilitate the transport of over 1.4m containers annually, reducing transit time across the country to less than six hours from port to port.
Israel Conflict
The ongoing conflict in the Middle East, particularly involving Israel, poses significant risks to global supply chains, raw material availability, and overall market stability. European manufacturing companies, heavily reliant on stable trade routes and secure energy supplies, may face disruptions due to heightened geopolitical tensions, shipping delays, and increased costs. This instability could prompt companies to reconsider their supply chain strategies, seeking alternative locations with greater security and logistical reliability.
Pandemic
The main trigger behind the nearshoring boom is the COVID-19 pandemic. For decades, international companies shifted production to China due to its low costs, large market, and strong trade relations with the U.S. However, the pandemic further exposed these weaknesses, as lockdowns, border closures, and workforce disruptions affected global production, transportation, and delivery times. Europe, heavily reliant on Asia, realized the risks of this dependence.
While challenges such as infrastructure constraints and security risks remain, continued improvements and a favorable economic climate further enhance Mexico's appeal as a dependable hub for global trade and industrial growth.





