
Economic Opportunities in Mexico

Mexico stands prominently within the upper ranks of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) attraction, securing a coveted position within the top 10. This accomplishment is underpinned by its economically strategic and geographically advantageous location, rendering it a paramount choice for manufacturing and evolving into a robust logistical hub. Boasting an extensive network of over 55 border crossings, coupled with a portfolio of over ten highly functional container ports, an extensive railway network spanning an impressive 16,800 miles, and a comprehensive network of over 80,000 miles encompassing highways and strategic trade routes, Mexico unassailably commands global precedence across numerous industries. This prowess translates into a commendable standing as one of the world's foremost exporters, consistently ranking within the top 15 nations in this pivotal economic facet.
- test content
- test content
Why is Mexico an attractive investment destination?
In a study published by Deloitte in July 2023, Mexico is not only attractive manufacturing destination since the main events occurred like Covid-19, USA-China Commercial tension or the Ukraine war. Other factors which are in favor of the country and contribute to the growing economy are US nearness, competitive salaries, qualified labor force or modern infrastructure.
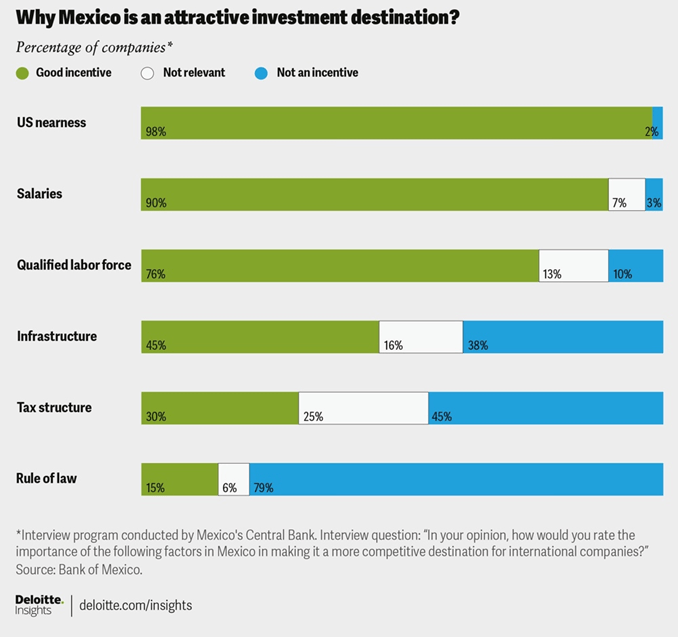
The nearshoring boom as economic driver
The global economic landscape has witnessed a paradigm shift as the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and trade disruptions prompted businesses to reconsider their supply chain strategies. Among the emerging trends, the nearshoring of manufacturing to Mexico has gained considerable momentum and is the economic driver of the country. This article delves into the multifaceted factors propelling this trend, including Mexico's strategic advantages, the USMCA trade agreement, evolving labor dynamics, and real estate considerations. By understanding the dynamics of Mexico's economic opportunities, we shed light on how businesses are positioning themselves in a post-pandemic world.
As we can extract from the graph below, there are three main events which affected Mexico’s growth positively; US tariffs on China in 2018, the Covid-19, and the present Russia-Ukraine war.
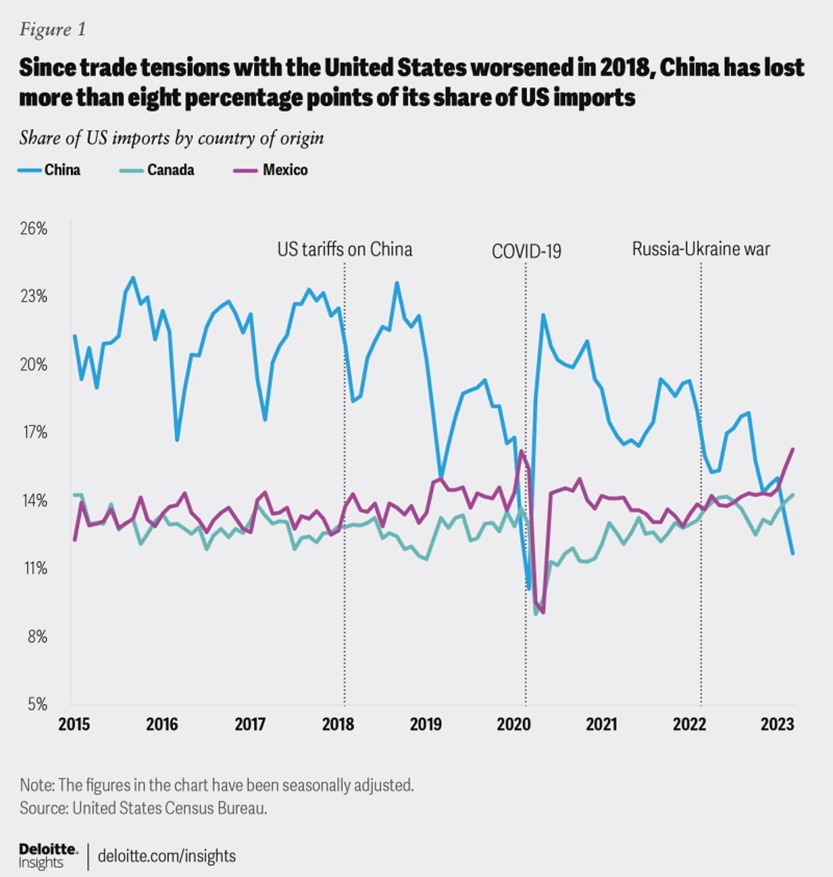
Indeed, The post-pandemic era has ushered in a profound and lasting transformation in the global economy, signaling the end of traditional supply chain dynamics. As a result of the disruption caused by the pandemic, China's dominant role in global manufacturing has shifted, prompting businesses to seek alternative production hubs. One significant shift is unfolding in Mexico, where a burgeoning industrial park has attracted the attention of Chinese companies seeking new bases of operation.
The trend has been particularly pronounced in Nuevo León, Mexico, where a surge of Chinese companies has been setting up factories and accelerates the economic development in Nuevo Leon (state of Monterrey). These businesses are motivated by the benefits of reduced transportation costs, proximity to the U.S. market, and participation in free trade agreements. This move is especially relevant for industries such as furniture, electronics, and clothing, which benefit from rapid transportation and duty-free access to North American markets.
What other factors accelerate Mexicos economic growth?
Mexico's geographical proximity to the colossal U.S. market has catapulted it to the forefront of nearshoring considerations. Unlike their Asian counterparts grappling with extended shipping times, companies nearshoring to Mexico benefit from reduced production-to-consumer timelines. This geographical advantage not only ensures efficient delivery but also empowers businesses to promptly respond to shifting market demands, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
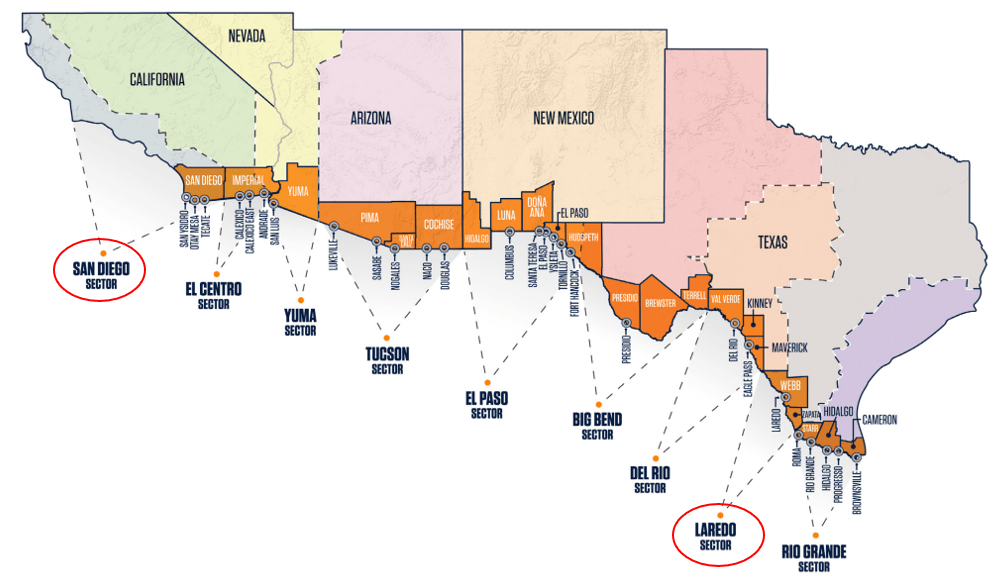
The extensive U.S.-Mexico border, featuring over 55 border crossings spanning its 2,000-mile stretch, facilitates expedited transportation. Notably, the Laredo, Texas border crossing emerges as a pivotal gateway, accommodating more than 30% of all U.S. imports. Furthermore, the surge in e-commerce amplifies Mexico's competitive edge, rendering it an appealing option for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chains.
USMCA Trade Agreement: Incentives and Influence
The USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) Trade Agreement, succeeding NAFTA, has wielded a profound influence on nearshoring dynamics and makes it attractive for foreign companies to invest into Mexico. By extending duty-free and value-added tax incentives to qualified products, the agreement has incentivized businesses to explore Mexico as a manufacturing hub. These incentives facilitate seamless importation of goods into the U.S. from Mexico, bolstering cost-efficiency and endowing supply chains with greater agility.
Experts from Colliers, a real estate leader, highlight how this trade agreement has reshaped operational strategies. Foreign manufacturers now harness the Port of Long Beach/Los Angeles to transport goods to Mexico duty-free. Subsequently, products undergo assembly or packaging in Mexico before being exported to the U.S., circumventing duties. Notably, the automotive sector, compelled by the USMCA's stipulation that 75% of automotive parts originate within North America, has played a pivotal role in driving Mexico's nearshoring wave and economic growth. Beyond automotive, industries encompassing appliances, plastics, and metal mechanics have witnessed noteworthy activity.
Geopolitical Considerations: A Risk Mitigation Strategy
In an era marked by geopolitical uncertainties, tariff fluctuations, and intellectual property concerns, companies have sought manufacturing alternatives to mitigate potential risks. Mexico, with its relative stability and proximity to the North American market, has emerged as a strategic choice. Shifting manufacturing operations to Mexico enables companies to minimize their exposure to these uncertainties, while simultaneously tapping into the advantages of nearshoring.
Evolving Labor Dynamics: Mexico's Skilled Workforce
Mexico's skilled and competitive labor force of nearly 60 million people, backed by favorable labor laws and competitive wages, attracts investors seeking access to a diverse talent pool. Indeed, the countries’ labor landscape has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from low-cost assembly to encompass diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, and high-tech manufacturing. Boasting competitive wages, a robust educational system, technical training programs, and English proficiency, Mexico presents an attractive proposition for companies seeking to expand their operations.
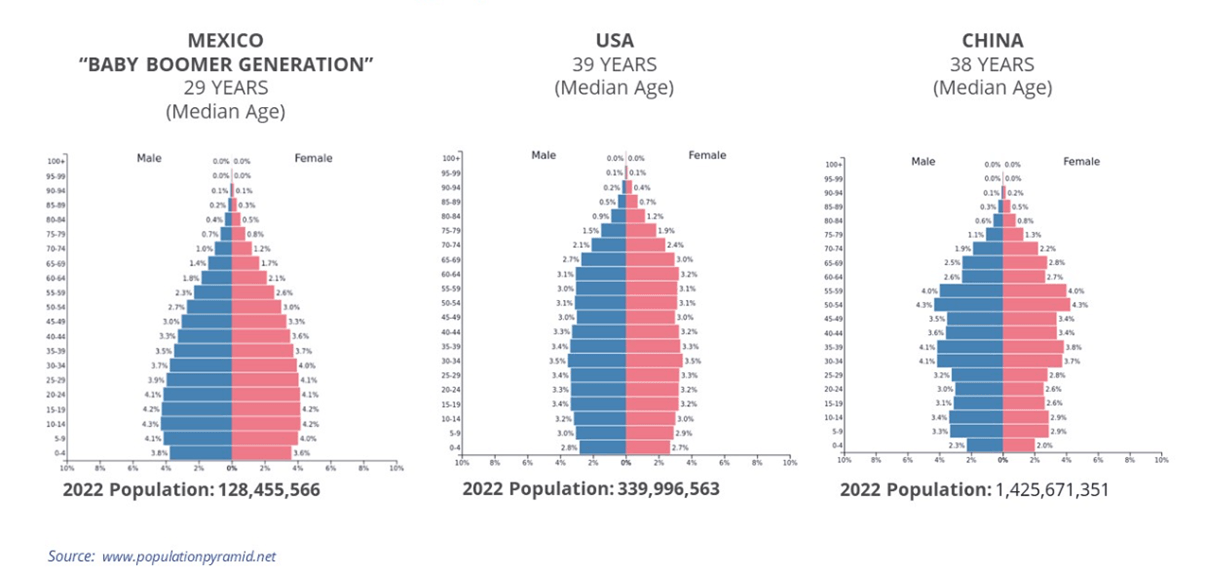
With an average age of 29, Mexico's youthful workforce is increasingly sought after, especially as the U.S. witnesses the retirement of its baby boomer generation. This demographic advantage, coupled with Mexico's evolving skill set, positions the country as a hub for cutting-edge manufacturing.
Real Estate Dynamics: Lease vs. Own
While leasing facilities is the preferred option for most companies in Mexico, distinctions emerge when examining preferences across different regions. Asian companies, for instance, lean toward property ownership. This divergence in strategy underscores the versatility within Mexico's real estate landscape. Existing spec buildings offer swift availability, catering to immediate operational needs, while build-to-suit options cater to intricate manufacturing processes, aligning facility choices with business objectives.
Mapping the Impact: Nearshoring's Influence
Visualizing the impact of nearshoring, a dynamic map showcases the regions and global corporations participating in Mexico's economic transformation. This map, which adapts to the evolving economic climate, reflects the agility and resilience of businesses post-pandemic. As Mexico capitalizes on its strategic advantages, it not only reshapes the global manufacturing landscape but also propels economic prosperity within the region.
Positive Forecast for Mexico’s Economy
Mexico's economic landscape is undergoing a significant transformation and growth, buoyed by promising projections and attractive investment opportunities. According to recent reports, the Mexican economy is predicted to achieve growth rates of up to 3.0% for the current year and the subsequent year. This economic potential is underpinned by increased investment in the manufacturing sector and a reduction in inflation, fueling the country's economic expansion.
Mexico's robust economy, with a population of nearly 130 million, ranks among the world's top 15, boasting a GDP of over $1.2 trillion. Its strategic location, rich natural resources, and thriving sectors like automotive and technology make it a prime investment destination. With increasing consumer purchasing power and attractive incentives for foreign investors, Mexico offers diverse opportunities for businesses looking to expand globally. The nation's trajectory is further bolstered by rising consumer buying capacity and alluring incentives tailored to attract foreign investors. For enterprises seeking international expansion, Mexico presents a multifaceted landscape of economic opportunities.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has revised its growth forecast for the Mexican economy in 2023 to 2.6%, a tenth of a percentage point higher than its previous prediction in November. This projection is slightly below the forecasts of the Mexican Secretary of Finance and Public Credit, Rogelio Ramírez de la O, who has anticipated a 3% growth rate by year-end. In its latest report, the OECD maintains its growth estimate for the Mexican economy in 2024 at 2.1%.
The report from the multilateral organization stated, "Consumption will be supported by improvements in the labor market but will be impacted by high inflation." However, the report also pointed out that inflation is expected to decrease from 5.9% in 2023 to 3.7% in 2024. The OECD cautioned that while the rise in prices has begun to moderate, expectations and underlying inflation remain elevated. Consequently, the report suggests that the monetary policy of the Bank of Mexico should remain "restrictive" and not initiate a gradual reduction in interest rates "until the end of 2023."
Additionally, the OECD emphasized that investment will continue to rise due to improvements in global value chain bottlenecks and the relocation of manufacturing activity to Mexico. The report highlighted the importance of reinforcing "regulatory certainty, especially in the energy sector," to maximize the benefits of ongoing processes of relocation to the country. Meanwhile, according to an analysis by Citibanamex, analysts have revised their estimate for Mexico's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth in 2023 to 2%.
Mexican Labor market boost economy
The labor market has displayed remarkable resilience and dynamism in its post-pandemic recovery phase, boasting historically low unemployment rates, well-contained levels of informal employment, an upswing in real wages, and a notable surge in the establishment of formal job positions.
Based on data sourced from the National Job and Employment Survey (ENOE), the currently employed workforce has surpassed pre-pandemic levels recorded back in February 2020 by a notable 5.7%. This growth equates to the creation of 3.2 million jobs and contributes a significant share for the Mexicans economic growth. It is distributed across various categories: 64.8% representing paid subordinate workers, 13.7% employers, 13.8% self-employed individuals, and 8.7% unpaid workers. This employment expansion has been accompanied by the lowest unemployment rates witnessed since 2005. Throughout the months of January to April 2023 (seasonally adjusted, sa), the average unemployment rate remained steady at 2.8%, marking a noteworthy reduction of 1.4 percentage points (pp) when compared to the historical pre-pandemic average. An equally significant facet of this employment landscape is the encouraging performance of the informal labor rate, which has experienced positive trends. The average informality rate for the initial four months of the year stood at 55.1% (sa), indicating a significant decrease of 3.3 pp in comparison to the historical average pre-pandemic.
Job creation contributes to economic progress
Formal employment, as evidenced by data from the Mexican Social Security Institute (IMSS) in the graph below, has showcased record figures in terms of job creation. The period spanning from January to May 2023 witnessed the generation of a total of 490 thousand new jobs, marking the highest recorded absolute figure since 1998. Furthermore, the growth in formal employment during the same period of the preceding year reached 2.3%, surpassing the rates of the prior two years by 0.4 pp and 0.2 pp respectively. This positive trajectory indicates a consistent pattern of growth. Particularly noteworthy is the substantial increase of 12.0% in the average real wage of IMSS-registered workers, surpassing pre-pandemic levels. This growth has been underpinned by elevations in the minimum wage and wage negotiations that have exceeded inflation rates. This, combined with the creation of 2.3 million jobs since August 2020 (commencing the recovery from pandemic-induced employment losses), has contributed significantly to an 18.8% growth in the total wage bill as of February 2020, thereby directly influencing household consumption.
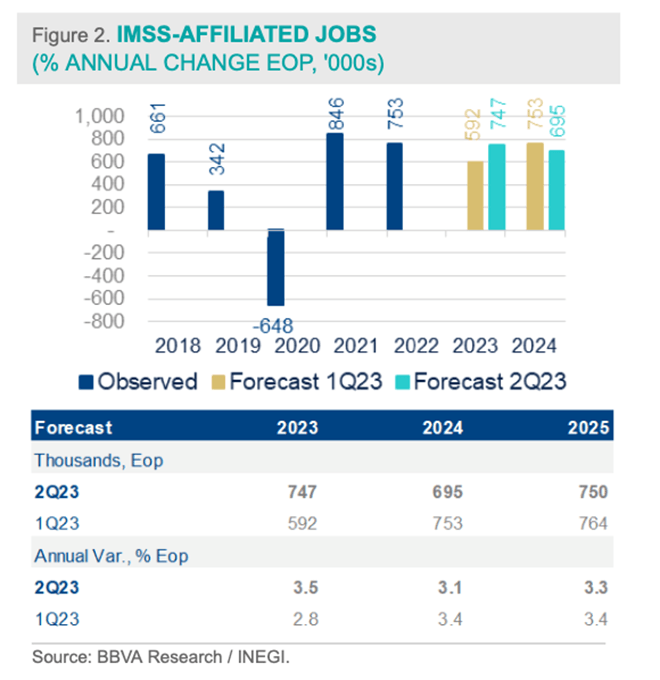
Building upon these encouraging trends and incorporating the upward revision of our growth projections, we anticipate a more optimistic outlook for formal job creation throughout this year. Our forecast suggests the addition of 747 thousand new jobs, signifying a year-on-year growth of 3.5% by the end of the year. In contrast, for the year 2024, a downward adjustment is expected, with a projected creation of 695 thousand new jobs, translating to a year-on-year growth of 3.1%
Stable economy thanks to strong Mexican peso
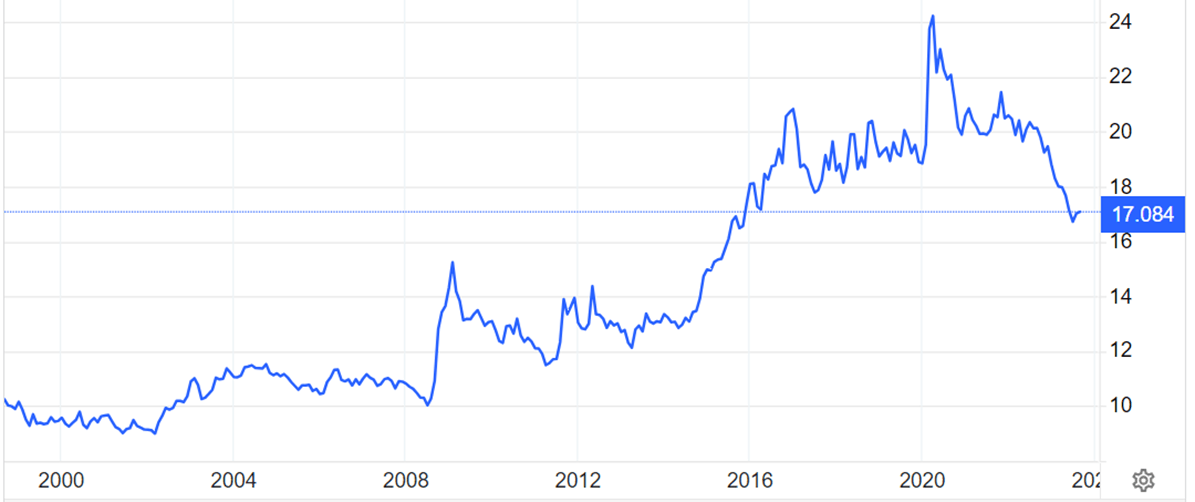
The Mexican peso's surprising strength has been a highlight this year, with analysts continually revising their exchange rate forecasts, now estimating it at 17.88 pesos per dollar, down from the previous projection of 17.95.
After prompt actions taken by various economic authorities to mitigate the international financial risks linked to issues in certain regional banks in the United States and Credit Suisse in Europe, the Mexican peso has resumed its trend of gaining value that it had been displaying since the start of the year. Factors like the significant interest rate gap with the United States, fiscal stability, and the prospect of minimal current account deficits in the near- and medium-term help to explain the robustness exhibited by the Mexican peso in recent months. As we foresee a positive inflation difference between Mexico and the United States by the close of 2023, and the interest rate differential with the United States to narrow in the years 2023-24, we predict a gradual decline in the peso's value, resulting in an exchange rate of 18.5 pesos per dollar by the conclusion of this year.
As the diagram reveals, the dollar has been lost on value by almost 30% in the last three years (2020 vs 2023)
 According to the "Citibanamex Expectations Survey," among 33 participants, BNP Paribas holds the most optimistic estimate for 2023 at 16.70 pesos per dollar, followed by XP Investments at 16.95 and HSBC at 17.00 pesos per US dollar. On the other end, Morgan Stanley has the highest estimate for the exchange rate in 2023 at 18.70 pesos per dollar, followed by Bursamétrica at 18.65, and Bancoppel, Invex, and Marasi Casa de Bolsa at 18.50.
According to the "Citibanamex Expectations Survey," among 33 participants, BNP Paribas holds the most optimistic estimate for 2023 at 16.70 pesos per dollar, followed by XP Investments at 16.95 and HSBC at 17.00 pesos per US dollar. On the other end, Morgan Stanley has the highest estimate for the exchange rate in 2023 at 18.70 pesos per dollar, followed by Bursamétrica at 18.65, and Bancoppel, Invex, and Marasi Casa de Bolsa at 18.50.
For 2024, analysts consulted by Citibanamex expect the Mexican peso to be at 19.00 pesos per dollar, slightly below the 19.03 predicted in the survey two weeks earlier. Bank of America Securities (BofA) suggests that the optimal scenario for the Mexican currency involves maintaining high interest rate differentials with the United States and the US economy avoiding a recession. BofA believes that this combination would keep carry trade attractive and volatility low, providing ongoing support to the peso's resilience. Despite potential risks of a deeper recession in the US economy, BofA still sees a favorable environment for the peso due to its carry trade appeal.
In recent trading, the peso closed with a 0.14% appreciation, trading around 17.06 pesos per dollar. This movement was attributed to market anticipation of relevant economic data releases, particularly in the United States, such as inflation data. The dollar's weakening during the session was driven by accommodative comments from officials of the Federal Reserve, suggesting that further interest rate hikes might not be necessary. The impact of Fitch Ratings' decision to downgrade the US credit rating has also been absorbed by the market, leading to increased risk appetite and a stronger dollar in the previous week.
Ready to take advantage of the Mexican growth opportunities?
Mexecution’s services support businesses to take advantage of the Mexican growth opportunities. With our site selection platform with high qualitative, available industrial spaces as well as pre-selected partners in areas such as lawyers, accounting, HR, Import & Export or Transportation, we help companies to expand successfully to Mexico.
Bibliography
Cervantes, D., Serrano, C., Amador, J., Rodríguez, A., Aránzazu, S., & Fernández, I. (June, 2023).Mexico Economic Outlook. June 2023. Retrieved from BBVA Research: https://www.bbvaresearch.com/en/publicaciones/mexico-economic-outlook-june-2023/#:~:text=Outlook%20for%20formal%20job%20creation,grade%20will%20be%20very%20limited.
Forbes Staff. (June, 2023). OCDE eleva a 2.6% su estimación de crecimiento económico para México en 2023.Retrieved from Forbes Mexico: https://www.forbes.com.mx/ocde-eleva-estimacion-crecimiento-economico-mexico-2023/
Goodman, P. S. (February, 2023). Why "Made in China" is becoming "Made in Mexico". (S. Tavernise, Entrevistador)
McCadden, R. (June, 2023). Nearshoring in Mexico: A Game-Changer for Manufacturing Operations. Retrieved from Colliers: https://knowledge-leader.colliers.com/rafael-mccaddencolliers-com/nearshoring-in-mexico-a-game-changer-for-manufacturing-operations/
Noguez, R. (August, 2023). El peso cerrará 2023 más fuerte de lo previsto, estas son las estimaciones. Retrieved from Forbes Mexico: https://www.forbes.com.mx/el-peso-cerrara-2023-mas-fuerte-de-lo-previsto-estas-son-las-estimaciones/
Zaga, D., & Ortiz, A. (July, 2023).Nearshoring in Mexico. Retrieved from Deloitte: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/economy/issues-by-the-numbers/advantages-of-nearshoring-mexico.html



