
Mexico’s Industrial Real Estate Market in 2025: Trends and Challenges

Nearshoring and Its Impact on Industrial Real Estate
The nearshoring movement, fueled by U.S. tariffs on China since 2018, has significantly benefited Mexico’s industrial sector. While the Biden administration upheld these tariffs and expanded restrictions on Chinese EVs and solar panels, concerns persist that China may leverage Mexico as a backdoor to the U.S. market.
President Trump has further linked tariffs on Mexican exports to broader issues like immigration and drug control. His push for an early renegotiation of the USMCA poses uncertainty for industrial real estate, as the sector heavily relies on export-driven manufacturing and logistics operations.

China’s Growing Role in Mexico’s Industrial Market
China’s industrial output continues to expand, with automotive production reaching 31 million units in 2024, according to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers. Amid a slowing domestic economy, China increased global exports by 12%, strengthening its presence in Mexico.
Chinese firms accounted for 27 million sq. ft. of industrial space absorption in Mexico between Q3-2021 and Q2-2024, averaging 9 million sq. ft. annually (13% of Mexico’s total industrial absorption). The peak was Q2-2022, when they acquired 4.8 million sq. ft. in just three months. This shift suggests that China’s reduced direct exports to the U.S. are partially offset by manufacturing in Mexico, raising concerns in Washington about tariff-free Chinese EVs under the USMCA’s rules of origin.
Mexico’s Industrial Real Estate Vacancy Trends
Focusing on the key sub-markets mentioned earlier, which account for approximately two-thirds of the total industrial stock, Exhibit #1 provides an overview of Gross Absorption (the total volume of newly leased and purchased industrial space within a year) and Net Absorption (Gross Absorption minus vacated spaces during the same period).
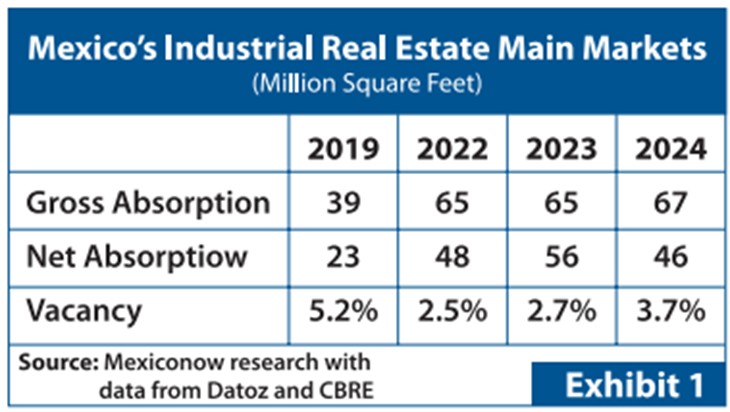
In 2024, the leaders in Gross Absorption were:
- Monterrey: 15 million sq. ft.
- Mexico City: 9 million sq. ft.
- Querétaro: 6 million sq. ft.
Meanwhile, the highest vacancy rates were recorded in:
- Ciudad Juárez: 10%
- Tijuana: 5.8%
- Reynosa: 5.3%
These vacancy levels reflect overzealous construction in 2024, anticipating nearshoring growth that did not fully materialize. Leasing activity from Chinese firms dropped from 6.5 million sq. ft. in 2023 to 3.7 million sq. ft. in 2024, signaling a slowdown in their nearshoring expansion.
Industrial Real Estate Prices and Rent Trends in Mexico
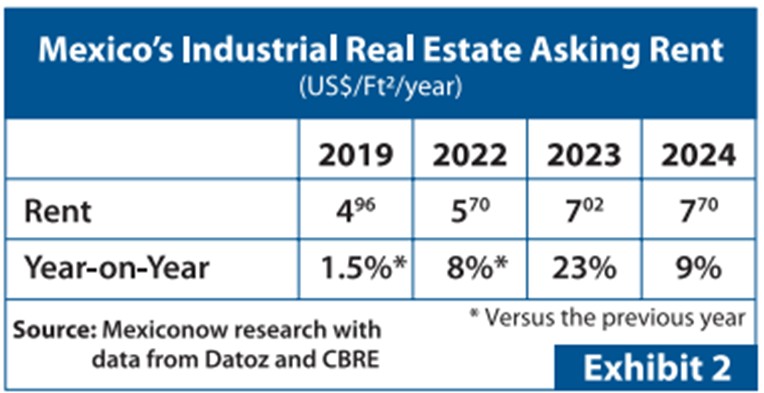
Lease rents surged 50% in five years, driven by two key factors:
- Nearshoring demand and a strong U.S. economy, which exhausted available space, especially in Mexico City and Monterrey.
- Rising construction costs, with steel prices soaring in 2022 due to China reducing export subsidies, alongside spikes in lumber, concrete, and copper.Prices later stabilized in 2024.
According to Cushman & Wakefield, in 2024, a 100,000 sq. ft. Class “A” distribution center in Guadalajara cost $80–$90 per sq. ft.
Industrial Real Estate Growth in Key Regions
Mexico’s industrial real estate stock grew 6% in 2024, reaching 1.11 billion sq. ft.Key regions with the highest growth:
- Monterrey: 12.5%
- Guadalajara: 10.5%
- Saltillo: 5.9%
- Tijuana: 5.6%
- Bajío region: 5.3%
- Ciudad Juárez: 3.2%
Monterrey and Saltillo captured 40% of nearshoring projects, while Mexico City saw an 11% stock increase, driven by logistics and e-commerce expansions, with major deals from DHL and Mercado Libre.
A major market shift was Prologis’ acquisition of Terrafina’s 41 million sq. ft. portfolio, solidifying its dominance with 90 million sq. ft. of industrial space, representing 8.1% of total market share.
Challenges Facing Mexico’s Industrial Real Estate: Energy, Security & Policy Risks
Despite growth, energy shortages remain a significant hurdle. Many projects faced delays due to insufficient electric power, a result of previous administrations' reluctance to invest in renewable energy. Over 25,000 MW of private-sector power projects remain stalled due to regulatory bottlenecks.
Security concerns are another issue, with frequent theft and transportation disruptions increasing operational costs and potentially discouraging nearshoring investment.
Outlook for Mexico’s Industrial Real Estate Market
2025 presents a mix of opportunities and risks.Key concerns include:
- Trump’s push to renegotiate the USMCA, potentially tightening rules of origin for Chinese EVs.
- Possible tariffs on Mexican exports, creating trade instability.
- A slight slowdown in nearshoring, leading to moderate increases in vacancy rates and possible rent stabilization.
However, Mexico’s cost-competitive labor market and strategic role in North American supply chains should prevent major disruptions. The next few months will be crucial as Mexico navigates shifting trade dynamics, energy constraints, and evolving policy risks.
Investors and businesses must remain adaptable, monitoring policy shifts and infrastructure improvements to sustain long-term success in Mexico’s industrial real estate sector.



