
USA Elections 2024: Why the USA Elections Won't Negatively Impact Mexico's Nearshoring Boom

Introduction: The Changing Face of U.S. Manufacturing and Nearshoring
As the 2024 USA elections approach, intense debates focus on the potential impact of a Trump-led administration versus other candidates on U.S. manufacturing. Despite political rhetoric and bold promises, the reality is that the United States is no longer the manufacturing powerhouse it once was. Instead, deep-rooted economic factors and an aging workforce have set the stage for companies to seek more efficient production alternatives—chief among them, Mexico.
In this context, the discussion of the USA Elections is less about abrupt policy shifts and more about long-term structural changes in global manufacturing.
Why the USA Elections Won't Derail Mexico's Nearshoring Boom
Historically, Trump’s policies—especially during the 2016 elections—played a pivotal role in accelerating Mexico's nearshoring boom. His tariff threats and aggressive stance on trade prompted companies to reexamine their supply-chain strategies, moving production closer to end markets.
However, whether Trump or his opponent is elected in 2024, several factors indicate that the U.S. manufacturing decline is irreversible. High labor costs, uncompetitive wages, and an aging workforce have long shifted production away from domestic manufacturing toward more cost-effective international alternatives.
The Impracticality of Drastic Tariff Increases
Despite the political posturing during election season, experts agree that it is highly unlikely for the U.S. to impose 50% or similarly steep tariffs on imports. The USMCA—by setting strict rules of origin—ensures that tariffs are balanced and negotiated collaboratively with key partners like Mexico and Canada.
This system protects American economic interests while maintaining robust trade relationships. In the context of the USA Election debates, such drastic measures would harm U.S. companies by disrupting global supply chains and retaliatory trade, thereby negating any short-term political gains.
Structural Shifts in U.S. Manufacturing
Data from reputable sources shows that traditional manufacturing in the United States has been in decline for decades. Studies indicate that 14 of the top 20 declining industries are in manufacturing, while service sectors such as healthcare, IT, and professional services are thriving. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the shift as companies pivoted toward more resilient and agile supply chains.
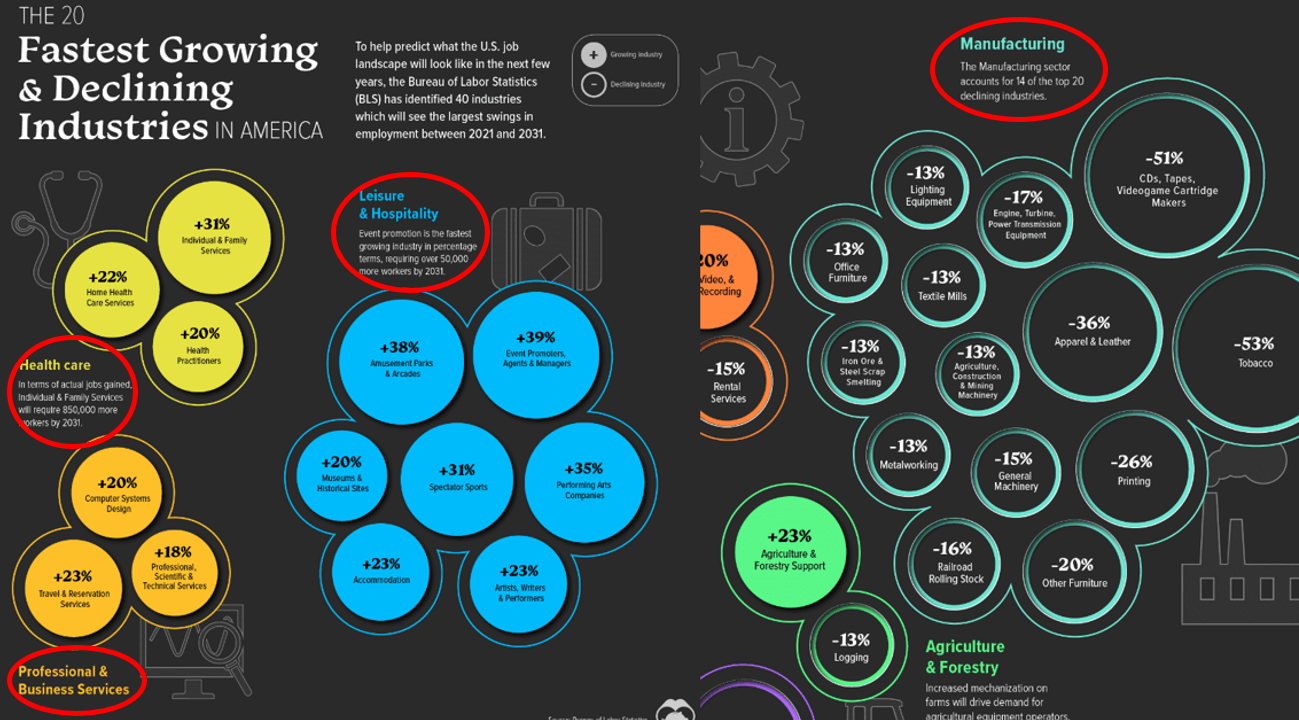
Future Outlook: Automation and Job Losses
As U.S. regulations and global competition favor high-tech and specialized manufacturing, the core of traditional manufacturing continues to erode, regardless of the outcome of Election discussions.
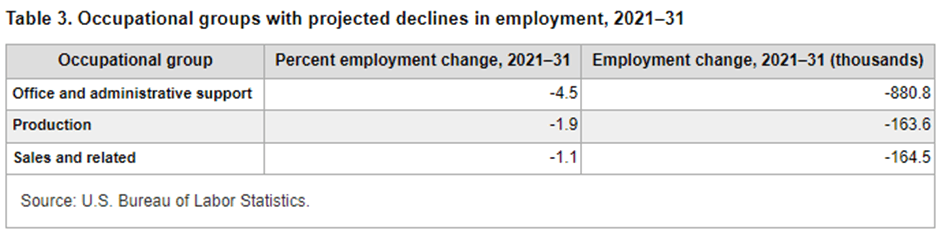
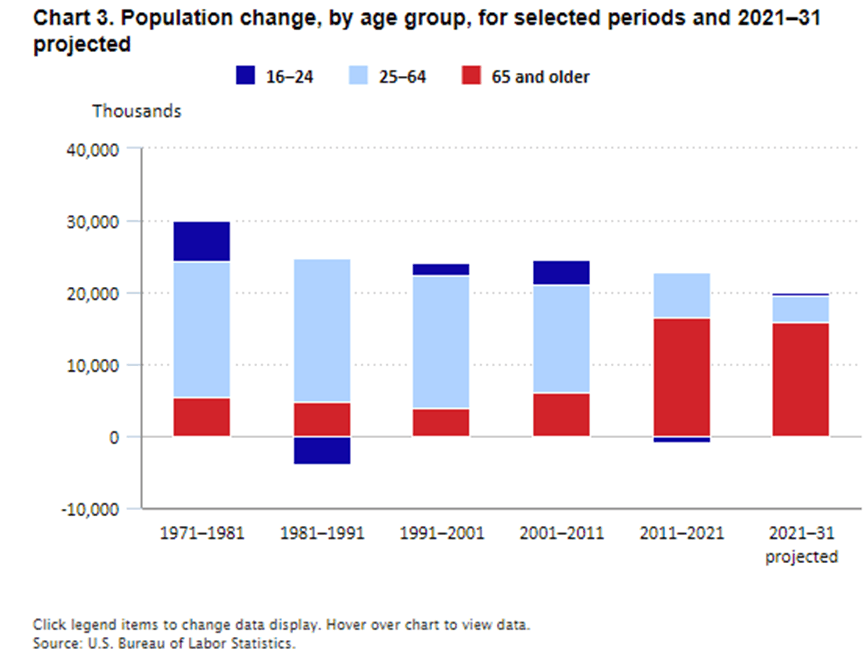
Between 2021 and 2031, automation and technology will likely lead to further declines; Many production roles are set to vanish, reinforcing the trend that the U.S. is moving away from traditional manufacturing.
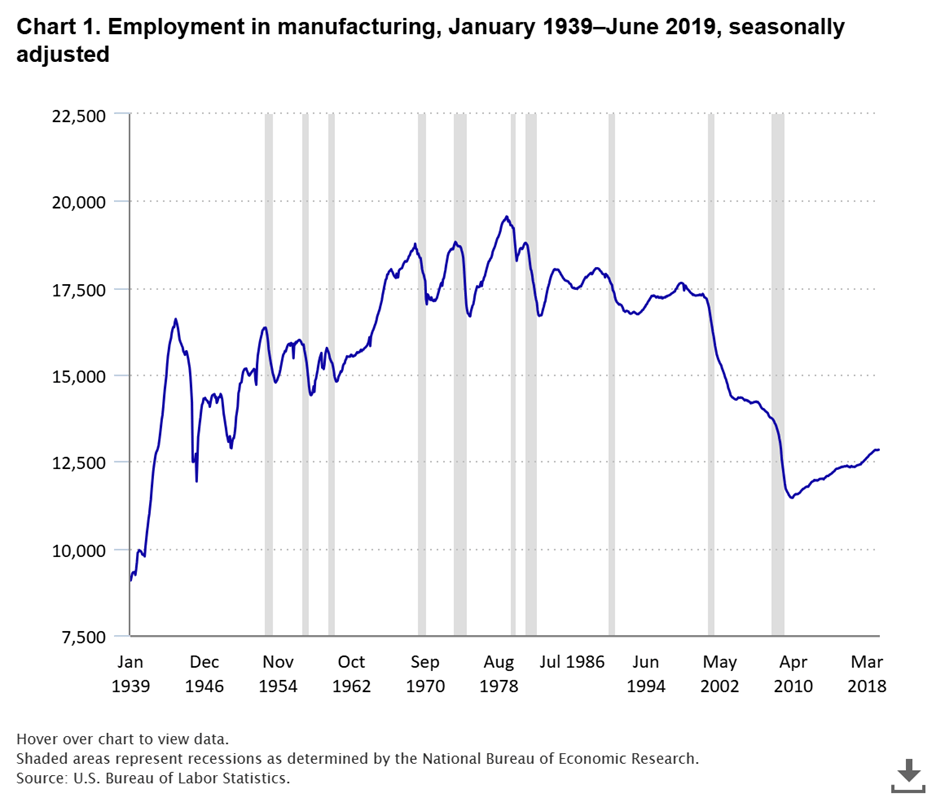
.
Aging Workforce and Slowed Labor Growth
With a rising median age and declining population growth, the U.S. labor force is shrinking. In contrast, Mexico’s youthful demographic provides a competitive edge for companies looking to invest in nearshoring operations.
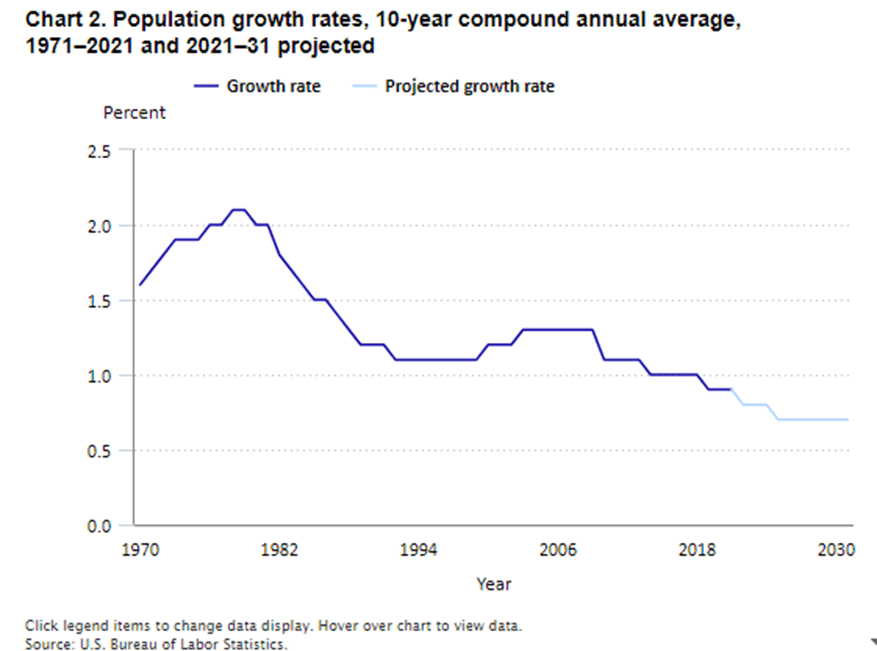
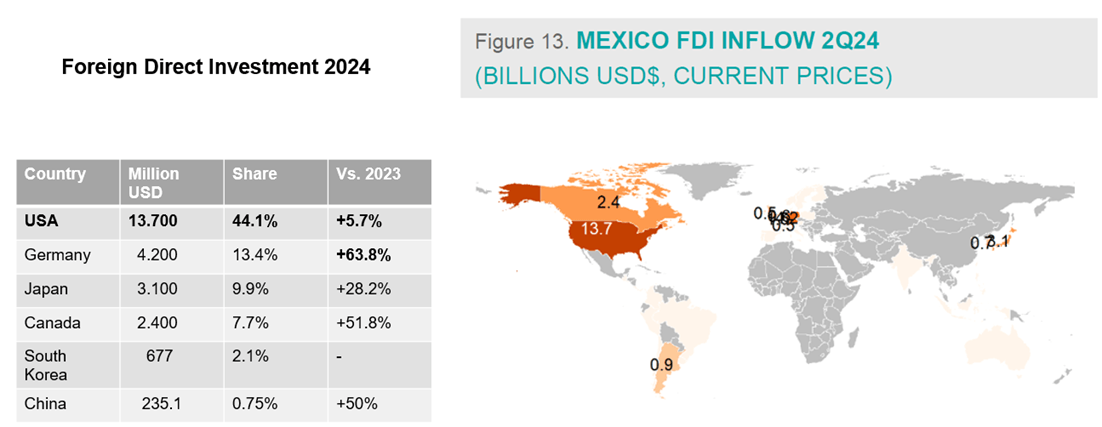
Continued U.S. Foreign Direct Investment in Mexico
Recent figures from 2Q24 highlight that American companies remain committed to investing in Mexico. With U.S. firms contributing over 44% of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Mexico—and significant investments already recorded in 2022 and 2023—it is evident that businesses are prioritizing long-term operational efficiency over short-term political uncertainties.
This trend underscores that the political debates of the USA Election are unlikely to alter the economic calculus driving nearshoring decisions.
.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Structural Economic Change
While the 2024 bring spirited discussions about the USA Election, the underlying economic reality remains unchanged. The decline in U.S. manufacturing, driven by structural factors such as high labor costs and an aging workforce, ensures that companies will continue to seek alternative production hubs like Mexico.
As global supply chains evolve, the nearshoring boom in Mexico is set to persist—anchored by long-term economic trends rather than fleeting political promises.
Links
https://www.visualcapitalist.com/charted-americas-fastest-growing-industries-by-employment-change/
https://www.bls.gov/opub/btn/volume-9/forty-years-of-falling-manufacturing-employment.htm
https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2022/article/projections-overview-and-highlights-2021-31.htm
https://www.visualcapitalist.com/charted-americas-fastest-growing-industries-by-employment-change/
Source: BBVA Research with data from Ministry of Economy (SE)



